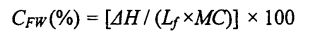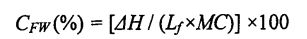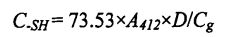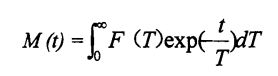കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടന രൂപീകരിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള മെറ്റീരിയൽ അടിസ്ഥാനമാണ് ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ. Experiments found that the addition of I--IPMC reduced the breakage of Yd and disulfide bonds between wheat gluten proteins during frozen storage. In addition, the results of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning the water state transition and recrystallization phenomena are limited, and the content of freezable water in the dough is reduced, thereby suppressing the effect of ice crystal growth on the gluten microstructure and its spatial conformation. Scanning electron microscope showed intuitively that the addition of HPMC could maintain the stability of gluten network structure.
കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഏറ്റവും കൂടുതൽ വരണ്ട കാര്യമാണ് അന്നജം, അതിന്റെ ഘടനയിലെ മാറ്റങ്ങൾ ജെലാറ്റിനൈനേഷൻ സവിശേഷതകളെയും അന്തിമ ഉൽപ്പന്നത്തിന്റെ ഗുണനിലവാരത്തെയും നേരിട്ട് ബാധിക്കും. X. എക്സ്-റേ ഡിഫ്രാക്ഷൻ, ഡിഎസ്സി എന്നിവയുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ അന്നജം വർദ്ധിച്ചതായും ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനൈനിറ്റിമാത നേറ്റപടതിനുശേഷം വർദ്ധിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന് ശേഷം വർദ്ധിച്ചുവെന്നും കാണിച്ചു. With the prolongation of frozen storage time, the swelling power of starch without HPMC addition decreased gradually, while the starch gelatinization characteristics (peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value and retrogradation value) all increased significantly; During the storage time, compared with the control group, with the increase of HPMC addition, the changes of starch crystal structure and gelatinization properties gradually decreased.
യീസ്റ്റിന്റെ അഴുകൽ ഗ്യാസ് പ്രൊഡക്ഷൻ പ്രവർത്തനത്തിന് പുളിപ്പിച്ച മാവ് ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളുടെ ഗുണനിലവാരത്തിൽ ഒരു പ്രധാന സ്വാധീനമുണ്ട്. Through experiments, it was found that, compared with the control group, the addition of HPMC could better maintain the fermentation activity of yeast and reduce the increase rate of extracellular reduced glutathione content after 60 days of freezing, and within a certain range, The protective effect of HPMC was positively correlated with its addition amount.
പ്രധാന വാക്കുകൾ: ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച റൊട്ടി; frozen dough; ഹൈഡ്രോക്സിപ്രോപൈൽ മെത്തിൽസെല്ലുലോസ്; wheat gluten; ഗോതമ്പ് അന്നജം; യീസ്റ്റ്.
ഉള്ളടക്ക പട്ടിക
1.1 വീട്ടിലും വിദേശത്തും ഗവേഷണ നില .......................................................................
1.1.2 Research status of steamed buns……………………………………………… . . ............ 1
1.1.3 ഫ്രോസൺ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ആമുഖം ............................................................................................. 2
1.1.4 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ .............................................................................................................................................
1.1.5 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... ........................................... 4 4
1.1.6 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഗുണനിലവാര മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്തലിൽ ഹൈഡ്രോക്കോളോയിഡുകളുടെ അപേക്ഷ ..................... .5
1.1.7 Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, I-IPMC) ………. 5
2.1 ആമുഖം .................................................................................................................. 8. 8
.
2.2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഉപകരണങ്ങളും ഉപകരണങ്ങളും ................................................................................................. 8
2.3 Experimental results and discussion…………………………………………………………………… . 11
2.3.1 ഗോതമ്പ് മാവിന്റെ അടിസ്ഥാന ഘടകങ്ങളുടെ സൂചിക ...................................................l
2.3.3 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ടെൻസൈൽ ഗുണങ്ങളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ സ്വാധീനം ................................ 12
2.3.4 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വഴുദനായ വാഞ്ഞുകളയിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സമയവും പ്രഭാവം ..................... ..............................................................................................................................................
2.3.6 ആവിയിൽ ബ്രെഡിന്റെ ഗുണനിലവാരത്തിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സമയവും .....................................................................................................................................1
2.4 അധ്യായം സംഗ്രഹം ........................................................................................................................
Chapter 3 Effects of HPMC addition on the structure and properties of wheat gluten protein under freezing conditions………………………………………………………………………………………...................24
3.2.1 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കൾ .......................................................................................... 25
3.2.4 Experimental methods ....................................................................................................... 25
3. ഫലങ്ങളും ചർച്ചയും ............................................................................................ 29
3.3.1 നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പിണ്ഡത്തിന്റെ വാഞ്ഞുകളയിലെ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും മരവിപ്പിക്കും.
3.3.2 മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന ഈർപ്പം (സിഎഫ്ഡബ്ല്യു), താപ സ്ഥിരത എന്നിവയിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ അളവ് ചേർത്ത് സംഭരണ സമയവും ചേർത്ത് പ്രാബല്യത്തിൽ ......................................... 30
3.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on free sulfhydryl content (C vessel) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 34
3.3.5 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the secondary structure of gluten………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….37
3.3.6 Effects of FIPMC addition amount and freezing time on the surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 41
Chapter 4 Effects of HPMC addition on starch structure and properties under frozen storage conditions………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 44
4.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................................. . 44
4.2 Experimental materials and methods ................................................................................. 45
4.2.1 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കൾ .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 45
4.2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഉപകരണം ........................................................................................................ 45
4.2.3 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക രീതി .............................................................................................. 45
4.3 Analysis and discussion ........................................................................................................... 48
4.3.1 Content of basic components of wheat starch ……………………………………………………. 48
4.3.2 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and frozen storage time on the gelatinization characteristics of wheat starch……………………………………………………………………………………………….48
4.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the shear viscosity of starch paste………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 52
4.3.5 Influence of HPMC addition amount and frozen storage time on starch swelling ability……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….56
4.3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and frozen storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 57
4.4 Chapter Summary ...................................................................................................................... 6 1
Chapter 5 Effects of HPMC addition on yeast survival rate and fermentation activity under frozen storage conditions………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 62
5.1Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 62
5.2 Materials and methods ............................................................................................................ 62
5.2.2 Experimental methods . . . . . ..................................................................... 63
5.3 Results and Discussion ............................................................................................................... 64
..3.2
5.3.3.3 1 " "
5.4 അധ്യായം സംഗ്രഹം ...................................................................................... 67
6.1 Conclusion ................................................................................................................................. . 68
6.2 lo ട്ട്ലുക്ക് ...................................................................................................... 68
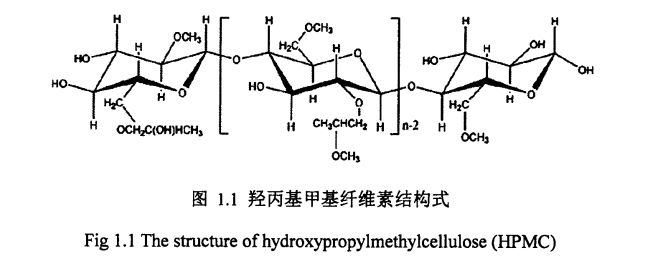
Figure 1.1 The structural formula of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose………………………. . 6
Figure 2.3 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the hardness of steamed bread……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... 19
Figure 2.4 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the elasticity of steamed bread………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 20
ചിത്രം 3.1 നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂട്ടന്റെ വാഞ്ഞുകലുള്ള എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സമയവും ..................................................................................... 30
ചിത്രം 3.2 . 34
Figure 3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing time on free sulfhydryl content of wheat gluten……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 35
ചിത്രം 3.5 ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രം ഡീകണേഷനും രണ്ടാമത്തെ ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് ഫിറ്റിംഗിനും ശേഷം ......................................................................... ... 38
ചിത്രം 3.7 മൈക്രോസ്കോപ്പിക് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും മരവിപ്പിക്കും. 43
ചിത്രം 4.1 അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ സ്വഭാവ വക്ര ......................................................................... 51
Figure 4.2 Fluid thixotropy of starch paste ................................................................................. 52
Figure 4.3 Effects of adding amount of MC and freezing time on the viscoelasticity of starch paste……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 57
Figure 4.5 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 59
ചിത്രം 5.1 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 2................................................................................................. ... 66
Figure 5.2 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the yeast survival rate…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 67
ചിത്രം. 68
ചിത്രം 5.4 ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ (ജിഎസ്എച്ച്) ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സമയവും .................................................................................................................................................
Table 2.1 The basic ingredient content of wheat flour…………………………………………………. 11
പട്ടിക 2.4 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യാനാകുമ്പോൾ (, സി.എഫ്.ആർ.എം.ജി.
പട്ടിക 2.5 വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡിന്റെ ടെക്സ്ചർ പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികളിൽ ഐ-ഐപിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയും സംഭരണ സമയവും ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുന്നു .........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................1.
Table 3.2 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the phase transition enthalpy (Yi IV) and freezer water content (e chat) of wet gluten………………………. 31
പട്ടിക 3.3 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ, ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ ഡിനാറ്ററേഷന്റെ പരമോന്നർ ഡിനാറ്ററേഷനിൽ സ്റ്റോറേജ് സമയം (.............................. 33
പട്ടിക 3.6 ഇ-ഐപിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെയും സ്റ്റോറേജ് സമയത്തിന്റെയും ഫലങ്ങൾ ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 41
പട്ടിക 4.2
പട്ടിക 4.3 ഗോതമ്പ് അന്നജം പേസ്റ്റിന്റെ കത്രാത്ത് വിസ്കോസിറ്റിയിലെ ഇഫക്റ്റിംഗ് സമയത്തിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ ................................................................................. 55
അധ്യായം 1 ആമുഖം
1.1.1 ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡിലേക്കുള്ള സ്ട്രോഡക്ഷൻ
പ്രകോപിതരായ റൊട്ടി പ്രൂഫിംഗിനും സ്റ്റീമിംഗിനും ശേഷം കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉണ്ടാക്കിയ ഭക്ഷണത്തെ സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. As a traditional Chinese pasta food, steamed bread has a long history and is known as "Oriental Bread". Because its finished product is hemispherical or elongated in shape, soft in taste, delicious in taste and rich in nutrients [l], it has been widely popular among the public for a long time. നമ്മുടെ രാജ്യത്തിന്റെ പ്രധാന ഭക്ഷണമാണിത്, പ്രത്യേകിച്ച് വടക്കൻ നിവാസികൾ. The consumption accounts for about 2/3 of the dietary structure of products in the north, and about 46% of the dietary structure of flour products in the country [21].
1.1.2 ന്റെ വേവിച്ച അപ്പത്തിന്റെ കാഴ്ച നില
നിലവിൽ, ആവിയിൽ റൊട്ടിയെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ഗവേഷണങ്ങൾ പ്രധാനമായും ഇനിപ്പറയുന്ന വശങ്ങളിൽ ശ്രദ്ധ കേന്ദ്രീകരിക്കുന്നു:
1) പുതിയ സ്വഭാവ സവിശേഷത ബണ്ണുകളുടെ വികസനം. Through the innovation of steamed bread raw materials and the addition of functional active substances, new varieties of steamed breads have been developed, which have both nutrition and function. പലവക ധാന്യഗതിയുടെ ആവിയിൽ ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച റൊട്ടിയുടെ വിലയിരുത്തൽ നിലവാരം സ്ഥാപിച്ചു; Fu e1. . ഹവോ & ബീറ്റ (2012) ബാർലി തവിട് പഠിച്ച ബാർലി തവിട്, ഫ്രോയിആീവ് വസ്തുക്കളിൽ (സമ്പന്നമായത്) [5]; ഷിയാ മീറ്റ് എ 1. .
3) കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ തയ്യാറെടുപ്പിനെയും ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡ് ടെക്നോളജിയെയും കുറിച്ച് ഗവേഷണം നടത്തുക. ആവിയിൽ ബ്രെഡ് പ്രൊഡക്ഷൻ പ്രോസസിന്റെ സ്വാധീനത്തെ അതിന്റെ ഗുണനിലവാരത്തിലും പ്രോസസ്സ് ഒപ്റ്റിമൈസേഷനിലും ഗവേഷണം നടത്തുക; ലിയു ചൻഹോംഗ് മറ്റുള്ളവരും. (2009) showed that in the process of dough conditioning, process parameters such as water addition, dough mixing time, and dough pH value have an impact on the whiteness value of steamed bread. It has a significant impact on sensory evaluation. പ്രോസസ് വ്യവസ്ഥകൾ അനുയോജ്യമല്ലെങ്കിൽ, ഉൽപ്പന്നം നീല, ഇരുണ്ട അല്ലെങ്കിൽ മഞ്ഞയായി മാറുന്നു. The research results show that during the dough preparation process, the amount of water added reaches 45%, and the dough mixing time is 5 minutes, ~ When the pH value of the dough was 6.5 for 10 min, the whiteness value and sensory evaluation of the steamed buns measured by the whiteness meter were the best. When rolling the dough 15-20 times at the same time, the dough is flaky, smooth, elastic and shiny surface; when the rolling ratio is 3:1, the dough sheet is shiny, and the whiteness of the steamed bread increases [l to; Li, et a1. (2015) explored the production process of compound fermented dough and its application in steamed bread processing [13].
4) ആവിയിൽ റൊട്ടിയുടെ ഗുണനിലവാര മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്തൽ സംബന്ധിച്ച ഗവേഷണം. ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡ് ക്രൗൺ വർഗീറ്റുകളുടെ സങ്കലനത്തെയും പ്രയോഗത്തെയും കുറിച്ചുള്ള ഗവേഷണം; mainly including additives (such as enzymes, emulsifiers, antioxidants, etc.) and other exogenous proteins [14], starch and modified starch [15], etc. The addition and optimization of the corresponding process It is particularly noteworthy that in recent years, through the use of some exogenous proteins and other additives, gluten-free (free. gluten) pasta products have been developed to meet the requirements of celiac disease (Dietary needs of patients with Coeliac Disease [16.1 cit.
5) ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച അപ്പത്തിന്റെയും അനുബന്ധ സംവിധാനങ്ങളുടെയും സംരക്ഷണവും ആന്റി-ഏജിംഗും. Pan Lijun et al. (2010) പരീക്ഷണാത്മക രൂപകൽപ്പനയിലൂടെ നല്ല വാർദ്ധക്യ പ്രഭാവം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് സംയോജിത മോഡിഫയർ ഒപ്റ്റിമൈസ് ചെയ്തു [ഞാൻ അങ്ങനെ ചെയ്യുന്നില്ല; വാങ്, ET A1. . The results showed that water loss and starch recrystallization were the main reasons for the aging of steamed bread [20].
6) പുതിയ പുളിപ്പിച്ച ബാക്ടീരിയയും പുളിയും എന്ന പ്രയോഗത്തെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ഗവേഷണം. ജിയാങ്, എറ്റ് എ 1. (2010) ചാഡോമിയം എസ്പിയുടെ പ്രയോഗം. സൈലാനേസ് (തെർമോസ്റ്റബിൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച്) ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച അപ്പത്തിൽ ഉത്പാദിപ്പിക്കാൻ പിഴെടുത്ത് [2L); ഗെറസ്, et a1. (2012) used two kinds of lactic acid bacteria in fermented flour products and evaluated their quality [221; Wu, et al. . ഗെറസ്, et a1. (2012) used the fermentation characteristics of two kinds of lactic acid bacteria to accelerate the hydrolysis of gliadin to reduce the allergenicity of flour products [24] and other aspects.
7) ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച അപ്പത്തിൽ ഗവേഷണം നടത്തുക.
അവയിൽ, ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച അപ്പം പരമ്പരാഗത സംഭരണ അവസ്ഥകൾക്ക് കീഴിലുള്ള വാർദ്ധക്യത്തിന് സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്, ഇത് ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡ് പ്രൊഡക്ഷൻ, പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് വ്യാവസായികവൽക്കരണം എന്നിവയുടെ വികസനത്തെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്ന ഒരു പ്രധാന ഘടകമാണ്. After aging, the quality of steamed bread is reduced - the texture becomes dry and hard, dregs, shrinks and cracks, the sensory quality and flavor deteriorate, the digestion and absorption rate decreases, and the nutritional value decreases. This not only affects its shelf life, but also creates a lot of waste. According to statistics, the annual loss due to aging is 3% of the output of flour products. 7%. ആളുകളുടെ ജീവിത നിലവാരവും ആരോഗ്യ വ്യവസായവും മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്തുന്നതിനൊപ്പം, ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡ് ഉൾപ്പെടെയുള്ള പരമ്പരാഗത പ്രചാരത്തിലുള്ള നൂഡിൽ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ, പുതിയ, ഉയർന്ന നിലവാരമുള്ളതും സൗകര്യപ്രദവുമായത്, എളുപ്പത്തിൽ സംരക്ഷണം എന്നിവയിൽ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ നേടുന്നതും വളരെക്കാലമായി സാങ്കേതിക പ്രശ്നമാണ്. ഈ പശ്ചാത്തലത്തെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി, ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നിലവിൽ വന്നു, അതിന്റെ വികസനം ഇപ്പോഴും സഖ്യത്തിലാണ്.
1.1.3 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ
1950 കളിൽ വികസിപ്പിച്ചെടുത്ത മാവ് ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളുടെ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗിനും ഉൽപാദനത്തിനുമുള്ള പുതിയ സാങ്കേതികവിദ്യയാണ് ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചത്. It mainly refers to the use of wheat flour as the main raw material and water or sugar as the main auxiliary materials. Baked, packed or unpacked, quick-freezing and other processes make the product reach a frozen state, and in. For products frozen at 18"C, the final product needs to be thawed, proofed, cooked, etc. [251].
a) ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ച രീതി: കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒരു കഷണം, ദ്രുതഗതിയിലുള്ളത്, ശീതീകരിച്ച, ഉരുകിയ, തെളിവ്, വേവിച്ച (ബേക്കിംഗ്, സ്റ്റീമിംഗ് മുതലായവ)
സി) പ്രീ-പ്രോസസ്ഡ് ഫ്രോസൺ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ: കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒരു കഷണങ്ങളായി തിരിച്ച് രൂപപ്പെടുത്തി, പൂർണ്ണമായി തെളിയിച്ചു, തുടർന്ന് (ഒരു പരിധിവരെ), തണുപ്പിക്കുക (ഒരു പരിധി വരെ), വേവിച്ച (ബേക്കിംഗ്, സ്റ്റീമിംഗ് മുതലായവ)
കേക്കുകൾക്കും മറ്റ് പാസ്ത ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾക്കും വ്യത്യസ്ത അളവിലുള്ള പ്രയോഗങ്ങളുണ്ട് [26-27]. According to incomplete statistics, by 1990, 80% of bakeries in the United States used frozen dough; 50% of bakeries in Japan also used frozen dough. ഇരുപതാം നൂറ്റാണ്ട്
ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ സാങ്കേതികവിദ്യ നിസ്സംശയമായും പരമ്പരാഗത ചൈനീസ് ഭക്ഷണത്തിന്റെ ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച റൊട്ടി പോലുള്ളവ. However, this processing technology still has some shortcomings, especially under the condition of longer freezing time, the final product will have longer proofing time, lower specific volume, higher hardness, Water loss, poor taste, reduced flavor, and quality deterioration. കൂടാതെ, ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുന്നതിനാലും
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത ഭക്ഷണങ്ങളിൽ ഐസ് പരലുകളുടെ രൂപീകരണവും വളർച്ചയും ഉൽപ്പന്ന നിലവാരത്തിന്റെ അപചയത്തിലേക്ക് നയിക്കുന്ന ഒരു പ്രധാന ഘടകമാണെന്ന് മിക്ക പഠനങ്ങളും കണ്ടെത്തി [291]. ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലുകൾ യീസ്റ്റിന്റെ അതിജീവന നിരക്ക് കുറയ്ക്കുക മാത്രമല്ല, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ ശക്തിയെയും ദുർബലപ്പെടുത്തുകയും, അന്നജം ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റിയെയും ജെൽ ഘടനയെയും ബാധിക്കുകയും, അത് ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ ശേഷി കുറയ്ക്കുകയും ചെയ്യും. In addition, in the case of frozen storage, temperature fluctuations can cause ice crystals to grow due to recrystallization [30]. അതിനാൽ, ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ രൂപീകരണത്തിന്റെയും അന്നജം, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ, യീസ്റ്റ് എന്നിവയുടെ പ്രതികൂല ഫലങ്ങൾ എങ്ങനെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കാം, മുകളിലുള്ള പ്രശ്നങ്ങൾ പരിഹരിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള താക്കോലാണ്, അത് ഒരു ചൂടുള്ള ഗവേഷണ മേഖലയും ദിശയും കൂടിയാണ്. കഴിഞ്ഞ പത്ത് വർഷത്തിനിടയിൽ, പല ഗവേഷകരും ഈ ജോലിയിൽ ഏർപ്പെടുകയും ഫലപ്രദമായ ചില ഗവേഷണ ഫലങ്ങൾ നേടുകയും ചെയ്തു. However, there are still some gaps and some unresolved and controversial issues in this field, which need to be further explored, such as:
a) ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ സമയത്തിന്റെ വിപുലീകരണത്തിന്റെ ഗുണനിലവാരമുള്ള കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ എങ്ങനെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കാം, പ്രത്യേകിച്ചും കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ (അന്നജം, ഗ്ലൂട്ടൻ, യീസ്റ്റ്) എന്നിവയുടെ ഘടനയുടെ രൂപീകരണത്തിന്റെയും സവിശേഷതകളുടെയും സ്വാധീനം എങ്ങനെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കാം, ഇപ്പോഴും ഒരു പ്രശ്നമാണ്. ഈ ഗവേഷണ മേഖലയിലെ ഹോട്ട്സ്പോട്ടുകളും അടിസ്ഥാന പ്രശ്നങ്ങളും;
b) വ്യത്യസ്ത മാവ് ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളുടെ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ്, ഉൽപാദന സാങ്കേതികവിദ്യയിലും സൂത്രവാക്യത്തിലും ചില വ്യത്യാസങ്ങളുണ്ട്, വ്യത്യസ്ത ഉൽപ്പന്ന തരങ്ങളുമായി യോജിക്കുന്ന പ്രത്യേക ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഗവേഷണത്തിന്റെ അഭാവമുണ്ട്;
c)Expand, optimize and use new frozen dough quality improvers, which is conducive to the optimization of production enterprises and the innovation and cost control of product types. നിലവിൽ, അത് ഇപ്പോഴും കൂടുതൽ ശക്തിപ്പെടുത്തുകയും വിപുലീകരിക്കുകയും വേണം;
ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളുടെയും ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉൽപന്നങ്ങളുടെയും പ്രകോപനപരമ്പരയുടെയും ഗുണനിലവാര നിയന്ത്രണത്തിന്റെയും മെച്ചപ്പെട്ട ഗവേഷണത്തിന്റെയും ഗുണനിലവാരത്തിന്റെയും അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിലുള്ള ഗവേഷണങ്ങളുടെയും ഇത്തരം ഗവേഷണങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയുടെ അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിൽ അത്തരം ഗവേഷണങ്ങൾ. Specifically, the main domestic and foreign researches in recent years mainly focus on the following points:
i.Study the changes in the structure and properties of frozen dough with the extension of freezing storage time, in order to explore the reasons for the deterioration of product quality, especially the effect of ice crystallization on biological macromolecules (protein, starch, etc.), for example, ice crystallization. രൂപവത്കരണവും വളർച്ചയും ജലപ്രവർത്തനവും വിതരണവുമായുള്ള ബന്ധവും; ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ ഘടന, അനുരഞ്ജന, ഗുണങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയിലെ മാറ്റങ്ങൾ [31]; അന്നജം ഘടനയിലെയും ഗുണങ്ങളിലെയും മാറ്റങ്ങൾ; കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മൈക്രോടെക്രേറ്ററിലും അനുബന്ധ സ്വത്തുക്കളിലും മാറ്റങ്ങൾ മുതലായവ. 361.
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികളുടെ അപചയത്തിനുള്ള പ്രധാന കാരണങ്ങൾ ഇവ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു: 1) മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയിൽ, യീസ്റ്റിന്റെ നിലനിൽപ്പ്, അതിന്റെ അഴുകൽ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ എന്നിവ ഗണ്യമായി കുറയുന്നു; 2) കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ തുടർച്ചയായതും പൂർണ്ണവുമായ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടന നശിപ്പിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു, ഫലമായി കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വായു കൈവശം വയ്ക്കൽ. and the structural strength is greatly reduced.
Ii. Optimization of frozen dough production process, frozen storage conditions and formula. During the production of frozen dough, temperature control, proofing conditions, pre-freezing treatment, freezing rate, freezing conditions, moisture content, gluten protein content, and thawing methods will all affect the processing properties of frozen dough [37]. In general, higher freezing rates produce ice crystals that are smaller in size and more uniformly distributed, while lower freezing rates produce larger ice crystals that are not uniformly distributed. In addition, a lower freezing temperature even below the glass transition temperature (CTA) can effectively maintain its quality, but the cost is higher, and the actual production and cold chain transportation temperatures are usually small. കൂടാതെ, മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന താപനിലയുടെ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകൾ പുനർവിചിന്തലയത്തിന് കാരണമാകും, അത് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നിലവാരത്തെ ബാധിക്കും.
III. Using additives to improve the product quality of frozen dough. ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉൽപ്പന്ന നിലവാരം മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്തുന്നതിന്, ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, അഡിറ്റീവുകൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച്, അഡിറ്റീവുകൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച്, അഡിറ്റീവുകളുടെ ഉപയോഗം ഫലപ്രദവും വ്യാപകമായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നതുമായ രീതിയാണ്. , I), ഞാൻ, ട്രാൻസ്ഗ്ലൂറ്റാമില്ലേസ്, അമിലേസ്; ii) മോണോഗ്ലിസറൈഡ് സ്റ്റെയർറേറ്റ്, ഡാറ്റാം, എസ്എസ്എൽ, സിഎസ്എൽ, ഡാറ്റാത്, തുടങ്ങിയവ പോലുള്ള എമൽസിഫയറുകൾ; iii) ആന്റിഓക്സിഡന്റുകൾ, അസ്കോർബിക് ആസിഡ് മുതലായവ; iv) ഗ്വാർ ഗം, യെല്ലോ ഒറിജിജിയം, ഗം അറബിക്, കോൺജക് ഗം, സോഡിയം ആൽജിനേറ്റ് മുതലായവ പോലുള്ള പോളിസക്ചൈഡ് ഹൈഡ്രോകോളോയിഡുകൾ; v) other functional substances, such as Xu, et a1. .
Ⅳ. Breeding of antifreeze yeast and application of new yeast antifreeze [58-59]. സസാനോ, et a1. .
മൺസാക്ചറൈഡുകൾ (ഗ്ലൂക്കോസ്, റാംനോസ്, അറബിമൃഗങ്ങൾ, മന്നാസ് മുതലായ ഒരു പോളിസക്ചമൈഡ് ആണ് ഹൈഡ്രോകോൾഓയിഡിന്റെ രാസ സ്വഭാവം.) 0 വഴി [. 1-4. ഗ്ലൈക്കോസിഡിക് ബോണ്ട് അല്ലെങ്കിൽ / കൂടാതെ. 1--"6. Glycosidic bond or B. 1-4. Glycosidic bond and 0 [.1-3. The high molecular organic compound formed by the condensation of glycosidic bond has a rich variety and can be roughly divided into: ① Cellulose derivatives , such as methyl cellulose (MC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC); ② plant കോൺജാക് ഗം, ഗ്വാർ ഗം, ഗം അറബിക്; ③ സീവ്യേഡ് പോളിസാഗ്രറൈഡുകൾ; ④ controlling the migration, state and distribution of water in the food system. Therefore, the addition of hydrophilic colloids gives food Many functions, properties, and qualities of hydrocolloids are closely related to the interaction between polysaccharides and water and other macromolecular substances. At the same time, due to the multiple functions of thickening, stabilizing, and water retention, hydrocolloids are widely used to include in the food processing മാവ് ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളുടെ. വാങ് സിൻ മറ്റുള്ളവരും. (2007) കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഗ്ലാസ് പരിവർത്തന താപനിലയിൽ കടൽവ്യാധിപതി പോളി പാസിചൈഡുകൾ, ജെലാറ്റിൻ എന്നിവ ചേർക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ഫലം പഠിച്ചു [631. വാങ് യുഷെംഗ് എറ്റ്. (2013) വൈവിധ്യമാർന്ന ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിക് കൊളോയിഡുകളുടെ സംയോജനം ചേർത്തത് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒഴുക്ക് ഗണ്യമായി മാറ്റാൻ കഴിയും. Change the properties, improve the tensile strength of the dough, enhance the elasticity of the dough, but reduce the extensibility of the dough [delete.
1.1.7 ഹോഡ്രോക്സിപ്രോപൈൽ മെഥൈൽ സെല്ലുലോസ് (ഹൈഡ്രോക്സിപ്രോപൈൽ മെഥൈൽ സെല്ലുലോസ്, ഐ-ഐപിഎംസി)
ലീനിയർ മോളിക്യുലർ ചെയിരലും ക്രിസ്റ്റലീൻ ഘടനയിലും ഹൈഡ്രജൻ ബോണ്ടുകളുടെ അസ്തിത്വം കാരണം, സെല്ലുലോസിന് മോശം ജലാശയമുണ്ട്, ഇത് അതിന്റെ ആപ്ലിക്കേഷൻ ശ്രേണിയെ പരിമിതപ്പെടുത്തുന്നു. However, the presence of substituents on the side chain of HPMC breaks the intramolecular hydrogen bonds, making it more hydrophilic [66l], which can quickly swell in water and form a stable thick colloidal dispersion at low temperatures Tie. ഒരു സെല്ലുലോസ് ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് ആസ്ഥാനമായുള്ള ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിക് കൊളോയിഡ് എന്ന നിലയിൽ, മെറ്റീരിയലുകൾ, പാപ്പിൾകേക്കിംഗ്, ടെക്സ്റ്റൈൽസ്, സൗന്ദര്യവർദ്ധക വസ്തുക്കൾ, ഫാർമസ്യൂട്ടിക്കൽസ്, ഭക്ഷണം എന്നിവയിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി വ്യാപകമായി ഉപയോഗിച്ചു [6 71]. In particular, due to its unique reversible thermo-gelling properties, HPMC is often used as a capsule component for controlled release drugs; ഭക്ഷണത്തിൽ, എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഒരു സർഫാറ്റാന്ത്, കട്ടിയുള്ളവർ, എമൽസിഫയറുകൾ, എമൽസിഫയറുകൾ മുതലായവയായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. For example, the addition of HPMC can change the gelatinization characteristics of starch and reduce the gel strength of starch paste. , എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ഭക്ഷണത്തിലെ ഈർപ്പം നഷ്ടപ്പെടുത്താനും ബ്രെഡ് കോർഡിന്റെ കാഠിന്യം കുറയ്ക്കാനും ഫലപ്രദമായി റൊട്ടിയുടെ വാർദ്ധക്യത്തെ തടയാനും കഴിയും.
എച്ച്പിഎംസി പാസ്തയിൽ ഒരു പരിധിവരെ ഉപയോഗിച്ചിട്ടുണ്ടെങ്കിലും, ഇത് പ്രധാനമായും പ്രായമാകുന്ന ഏജന്റിനും വാട്ടർ-സ്ടെയ്നിംഗ് ഏജൻറ് ആയി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, ഗ്വാർ ഗം, സാന്താൻ ഗം, സോഡിയം ആൽജിനേറ്റ് [75-771] അതിന്റെ ഫലത്തെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള പ്രസക്തമായ റിപ്പോർട്ടുകളുടെ അഭാവമുണ്ട്.
1.2 റിയാൻഡ് ഉദ്ദേശ്യവും പ്രാധാന്യവും
At present, the application and large-scale production of frozen dough processing technology in my country as a whole is still in the development stage. അതേസമയം, ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുപയോഗിച്ച് ചില അപകടങ്ങളും കുറവുകളും ഉണ്ട്. These comprehensive factors undoubtedly restrict the further application and promotion of frozen dough. on the other hand,this also means that the application of frozen dough has great potential and broad prospects, especially from the perspective of combining frozen dough technology with the industrialized production of traditional Chinese noodles (non-)fermented staple food, to develop more products that meet the needs of Chinese residents. It is of practical significance to improve the quality of the frozen dough based on the characteristics of Chinese pastry and the dietary habits, and is suitable for the processing characteristics of Chinese pastry.
Effects of addition amount and frozen storage time on the structure and properties of frozen dough, the quality of frozen dough products (steamed bread), the structure and properties of wheat gluten, the structure and properties of wheat starch, and the fermentation activity of yeast. മേൽപ്പറഞ്ഞ പരിഗണനകളെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി, ഈ ഗവേഷണ വിഷയത്തിൽ ഇനിപ്പറയുന്ന പരീക്ഷണ രൂപകൽപ്പന നൽകി:
2) മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്തൽ സംവിധാനത്തിന്റെ വീക്ഷണകോണിൽ നിന്ന്, ആർദ്ര ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പിണ്ഡത്തിന്റെ വാഴയിലെ വ്യത്യസ്ത എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ, ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റനിലെ ഘടന, പ്രകാശം ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ ഘടന എന്നിവ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യൽ സംഭരണ സമയ വ്യവസ്ഥകളിൽ പഠിച്ചു.
4) മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്തൽ സംവിധാനത്തിന്റെ വീക്ഷണകോണിൽ നിന്ന്, അഴുകൽ പ്രവർത്തനത്തെ അതിജീവന നിരക്ക്, അതിജീവന നിരക്ക്, എക്സ്ട്രാക്കേസെല്ലുലാർ ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ എന്നിവ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യൽ സംഭരണ സമയ വ്യവസ്ഥകൾ പ്രകാരം പഠിച്ചു.
അധ്യായം 2 ഫ്രോസൺ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികളിലും ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡ് ഗുണനിലവാരത്തിലും
2.1 ആമുഖം
Generally speaking, the material composition of dough used for making fermented flour products mainly includes biological macromolecular substances (starch, protein), inorganic water, and yeast of organisms, and is formed after hydration, cross-linking and interaction. ഒരു പ്രത്യേക ഘടനയുള്ള സ്ഥിരതയുള്ളതും സങ്കീർണ്ണവുമായ ഭ material തിക സംവിധാനം വികസിപ്പിച്ചെടുത്തിട്ടുണ്ട്. കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ അന്തിമ ഉൽപ്പന്നത്തിന്റെ ഗുണനിലവാരത്തിൽ കാര്യമായ സ്വാധീനം ചെലുത്തുന്നുവെന്ന് നിരവധി പഠനങ്ങൾ തെളിയിച്ചിട്ടുണ്ട്. Therefore, by optimizing the compounding to meet the specific product and it is a research direction to improve the dough formulation and technology of the quality of the product or food for use; on the other hand, improving or improving the properties of dough processing and preservation to ensure or improve the quality of the product is also an important research issue.
ആമുഖത്തിൽ സൂചിപ്പിച്ചതുപോലെ, ഒരു കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒരു കുഴെച്ച ഗുണങ്ങൾ (ഫരീൻ, വലോംഗങ്ങൾ, വാരിയോളജി മുതലായവ) എന്നിവയിൽ സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു (ഫരീൻ, വലോഗം, വാഴ, വാടി, അന്തിമ ഉൽപ്പന്ന നിലവാരം എന്നിവയുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട രണ്ട് പഠനങ്ങളാണ്.
2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കളും രീതികളും
Zhongyu Wheat Flour Binzhou Zhongyu Food Co., Ltd.; Angel Active Dry Yeast Angel Yeast Co., Ltd.; HPMC (methyl substitution degree of 28%.30%, hydroxypropyl substitution degree of 7%.12%) Aladdin (Shanghai) Chemical Reagent Company; ഈ പരീക്ഷണത്തിൽ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന എല്ലാ രാസ റിയാക്ടറുകളും അനലിറ്റിക്കൽ ഗ്രേഡിലാണ്;
2.2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഉപകരണങ്ങളും ഉപകരണങ്ങളും
ഉപകരണവും ഉപകരണത്തിന്റെയും പേര്
BPS. 500 ക്ലൂ നിരന്തരമായ താപനിലയും ഈർപ്പം ബോക്സും
ടിഎ-എക്സ് ടി പ്ലസ് ഫിസിക്കൽ പ്രോപ്പർട്ടി ടെസ്റ്റർ
BSal24s ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് അനലിറ്റിക്കൽ ബാലൻസ്
Dhg. 9070A Blast Drying Oven
SM. 986S dough mixer
C21. KT2134 ഇൻഡക്ഷൻ കുക്കർ
Powder meter. ഇവ
എക്സ്റ്റൻസോമീറ്റർ. ഇവ
ഡിസ്കവറി ആർ 3 റൊട്ടഫർ റിമീറ്റർ
Q200 ഡിഫറൻഷ്യൽ സ്കാൻ ചെയ്യുന്നത് കലോറിമീറ്റർ
Sx2.4.10 മഫിൽ ചൂള
കെജെറ്റോറി ടിഎം 8400 ഓട്ടോമാറ്റിക് കെജെൽഡഹ്ൽ നൈട്രജൻ അനലൈസർ
നിര്മ്മാതാവ്
സാർട്ടോറിയസ്, ജർമ്മനി
ടോപ്പ് കിച്ചൻ അപ്ലയൻസ് ടെക്നോളജി കോ., ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ഗ്വാങ്ഡോംഗ് മിഡിയാ ലൈഫ് അപ്ലൈൻസ് മാനാവിക് രൂപ കോ.
ജർമ്മനി, ജർമ്മനി
ജർമ്മനി, ജർമ്മനി
അമേരിക്കൻ ടിഎ കമ്പനി
അമേരിക്കൻ ടിഎ കമ്പനി
ഹുവാങ് ഷി ഹെങ് ഫെങ് മെഡിക്കൽ ഉപകരണ കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
2.2.3 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക രീതി
2.2.3.1 മാവിന്റെ അടിസ്ഥാന ഘടകങ്ങളുടെ നിർണ്ണയം
റഫറൻസ് രീതി അനുസരിച്ച് ജിബി / ടി 14614.2006 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ [821] നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നത് [821.
DEG / T 14615.2006 അനുസരിച്ച് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ടെൻസൈൽ ഗുണങ്ങൾ നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നു [831.
2.2.4 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉത്പാദനം
GB / t 17320.1998 ന്റെ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നടത്തുന്നത് കാണുക [84]. Weigh 450 g of flour and 5 g of active dry yeast into the bowl of the dough mixer, stir at low speed to fully mix the two, and then add 245 mL of low-temperature (Distilled water (pre-stored in the refrigerator at 4°C for 24 hours to inhibit the activity of yeast), first stir at low speed for 1 min, then at medium speed for 4 min until dough is formed. Take out the dough and divide it into about 180g / portion, knead it into a cylindrical shape, then seal it with a ziplock bag, and put it in. Freeze at 18°C for 15, 30, and 60 days. Add 0.5%, 1%, 2% (w/w, dry basis) HPMC to replace the corresponding proportion of flour quality to make dough, and the rest of the production methods remain unchanged. The 0-day frozen storage (unfrozen storage) was used as the control experimental group.
2.2.3.5 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വാളായി നിർണ്ണയിക്കുക
അനുബന്ധ മരവിധ്യമുള്ള സമയത്തിന് ശേഷം കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ പുറത്തെടുക്കുക, അവ 4 മണിക്കൂർ 4 f ° C ൽ ഒരു റഫ്രിജറേറ്ററിൽ ഇടുക, തുടർന്ന് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉരുകുന്നതുവരെ room ഷ്മാവിൽ ഇടുക, തുടർന്ന് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉരുകുന്നതുവരെ rom ഷ്മാവിൽ ഇടുക. The sample processing method is also applicable to the experimental part of 2.3.6.
A sample (about 2 g) of the central part of the partially melted dough was cut and placed on the bottom plate of the rheometer (Discovery R3). First, the sample was subjected to dynamic strain scanning. The specific experimental parameters were set as follows: A parallel plate with a diameter of 40 mm was used, the gap was set to 1000 mln, the temperature was 25 °C, and the scanning range was 0.01%. 100%, സാമ്പിൾ വിശ്രമ സമയം 10 മിനിറ്റാണ്, ആവൃത്തി 1hz ആയി സജ്ജമാക്കി. പരീക്ഷിച്ച സാമ്പിളുകളുടെ ലീനിയർ വിസ്കോലാസ്റ്റിറ്റി മേഖല (എൽവിആർ) നിർണ്ണയിച്ചത് സ്ട്രെയിൻ സ്കാനിംഗ് ആണ്. Then, the sample was subjected to a dynamic frequency sweep, and the specific parameters were set as follows: the strain value was 0.5% (in the LVR range), the resting time, the fixture used, the spacing, and the temperature were all consistent with the strain sweep parameter settings. ഫ്രീക്വൻസി (ലീനിയർ മോഡ്) ഓരോ 10 മടങ്ങ് വർദ്ധനവിനും അഞ്ച് ഡാറ്റാ പോയിന്റുകൾ (പ്ലോട്ടുകൾ) രേഖപ്പെടുത്തി. After each clamp depression, the excess sample was gently scraped with a blade, and a layer of paraffin oil was applied to the edge of the sample to prevent water loss during the experiment. Each sample was repeated three times.
2.2.3.6 മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ (മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ ഉള്ളടക്കം)
അവയിൽ, the ഈർപ്പം ഒളിഞ്ഞിന്റെ ചൂടായ ചൂടിനെ പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നു, അതിന്റെ മൂല്യം 334 ജെ ഡാൻ; എംസി (ആകെ ഈർപ്പം ഉള്ള ഈർപ്പം) കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മൊത്തം ഈർപ്പം പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നു (ജിബി 50093.2010T78] അനുസരിച്ച് അളക്കുന്നു)). ഓരോ സാമ്പിളും മൂന്ന് തവണ ആവർത്തിച്ചു.
2.2.3.7 ആവിയിൽ ബ്രെഡ് പ്രൊഡക്ഷൻ
(1) ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച റൊട്ടിയുടെ നിർണ്ണയം
ജിബി / ടി 20981.2007 അനുസരിച്ച്, ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബണ്ണുകളുടെ അളവ് (ജോലി) അളക്കാൻ ബലാത്സംഗം ചെയ്ത ഡിപ്രാക്കേറ്റ് രീതി ഒരു ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് ബാലൻസ് ഉപയോഗിച്ച് അളന്നു. ഓരോ സാമ്പിളിലും മൂന്ന് തവണ പകർത്തി.
സിഎം, നൂർ അസിയാ, ചെംഗ് (2011] ന്റെ രീതി കാണുക. A 20x 20 x 20 mn'13 core sample of the steamed bread was cut from the central area of the steamed bread, and the TPA (Texture Profile Analysis) of the steamed bread was measured by a physical property tester. Specific parameters: the probe is P/100, the pre-measurement rate is 1 mm/s, the mid-measurement rate is 1 mm/s, the post-measurement rate is 1 mm/s, the compression deformation variable is 50%, and the time interval between two compressions is 30 S, the trigger force is 5 g. Each sample was repeated 6 times.
2.2.3.9 ഡാറ്റ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ്
All experiments were repeated at least three times unless otherwise specified, and the experimental results were expressed as the mean (Mean) ± standard deviation (Standard Deviation). എസ്പിഎസ്എസ് സ്ഥിതിവിവരക്കണക്ക് 19 പേരെ വേരിയൻസ് (വേരിയൻസ്, അനോവയുടെ വിശകലനം) എന്നിവയ്ക്കായി ഉപയോഗിച്ചു, കൂടാതെ പ്രാധാന്യം നില. 05; പ്രസക്തമായ ചാർട്ടുകൾ വരയ്ക്കാൻ ഉത്ഭവ 8.0 ഉപയോഗിക്കുക.
ടാബ് 2.1 ഗോതമ്പ് മാവിൽ പ്രാഥമിക ഘടകത്തിന്റെ ഉള്ളടക്കം
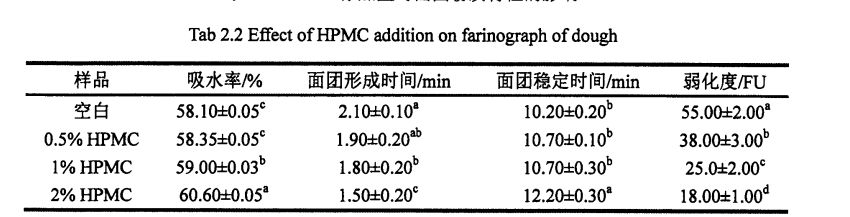
2.3.2 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഇ-ഐപിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ ഫലം
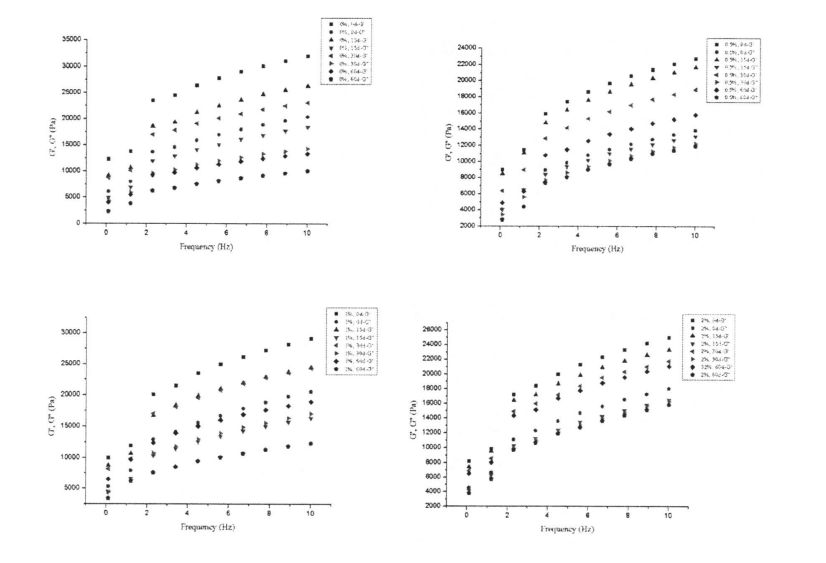
As shown in Table 2.2, with the increase of HPMC addition, the water absorption of dough increased significantly, from 58.10% (without adding HPMC dough) to 60.60% (adding 2% HPMC dough). In addition, the addition of HPMC improved the dough stability time from 10.2 min (blank) to 12.2 min (added 2% HPMC). എന്നിരുന്നാലും, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവും, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 55 മിനിറ്റ്, 55.0 FU എന്നിവ യഥാക്രമം കുറയുന്നു, ഇത് യഥാക്രമം 2.10 മിനിറ്റും 55.0 ഫുവിനും രൂപം കൊള്ളുന്നു, ഇത് യഥാക്രമം 28.57 ശതമാനവും 67.27 ശതമാനവും കുറഞ്ഞു.
കുറിപ്പ്: ഒരേ നിരയിലെ വ്യത്യസ്ത സൂപ്പർസ്ക്രിപ്റ്റ് ചെറിയ അക്ഷരങ്ങൾ പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ട വ്യത്യാസം സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു (പേജ് <0.05)
കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വേദപുസ്തകത്തിന്റെ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് സവിശേഷതകളെ പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുന്നതാണ്, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, ടെൻസൈൽ റെസിസ്റ്റൻസ്, സ്ട്രെച്ച് അനുപാതം എന്നിവ ഉൾപ്പെടെ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ കഴിക്കുന്നതാണ്. The tensile properties of the dough are attributed to the extension of the glutenin molecules in the dough extensibility, as the cross-linking of glutenin molecular chains determines the elasticity of the dough [921]. Termonia, Smith (1987) [93] believed that the elongation of polymers depends on two chemical kinetic processes, that is, the breaking of secondary bonds between molecular chains and the deformation of cross-linked molecular chains. തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ രൂപഭേദം കുറവായപ്പോൾ, തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ വലിച്ചുനീട്ടിയ സമ്മർദ്ദം തന്മാത്രയ്ക്ക് വേണ്ടത്ര വേഗത്തിൽ നേരിടാനാവില്ല, അത് തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ വേലിയേറ്റത്തിലേക്ക് നയിക്കുന്നു, കൂടാതെ തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ വേലക്കാറ്റും തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ രൂപഭേദം അപകർഷതാബോധം വേഗത്തിലും വേണ്ടത്രയും വികൃതമാകുമ്പോഴും, തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയിലെ കോവാന്റ് ബോണ്ട് നോഡുകൾ തകർക്കാൻ കഴിയുമ്പോഴും, പോളിമറിന്റെ നീളം വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കില്ല. അതിനാൽ, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ ചെയിൻവിന്റെ രൂപഭേദം, നീളമേറിയ പെരുമാറ്റം മാറ്റുന്നത് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ [92] ന്റെ ടെൻസൈൽ ഗുണങ്ങളിൽ സ്വാധീനം ചെലുത്തും.
ജെ (2% എച്ച്പിഎംസിഐ ചേർത്തു). At the same time, the maximum tensile resistance of the dough decreased from 674.50-a: 34.58 BU (blank) to 591.80--a: 5.87 BU (adding 0.5% HPMC), 602.70± 16.40 BU (1% HPMC added), and 515.40-a: 7.78 BU (2% HPMC added). However, the elongation of the dough increased from 154.75+7.57 MITI (blank) to 164.70-a: 2.55 m/rl(adding 0.5% HPMC), 162.90-a: 4 .05 min (1% HPMC added), and 1 67.20-a: 1.98 min (2% HPMC added). This may be due to the increase of the plasticizer-water content by adding HPMC, which reduces the resistance to the deformation of the gluten protein molecular chain, or the interaction between HPMC and the gluten protein molecular chain changes its stretching behavior, which in turn affects It improves the tensile properties of the dough and increases the extensibility of the dough, which will affect the quality (eg, specific volume, അവസാന ഉൽപ്പന്നത്തിന്റെ ഘടന.
2.3.4 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ അളവിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വാരുപ്പേര്
കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, വിസ്കോലാസ്റ്റിക്, സ്ഥിരത, പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് സവിശേഷതകൾ, പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ്, സംഭരണം സമയത്ത്, സ്വത്തുക്കൾ എന്നിവയുടെ സമഗ്രമായ സവിശേഷതകളെ ആസൂത്രിതമായി പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കും.
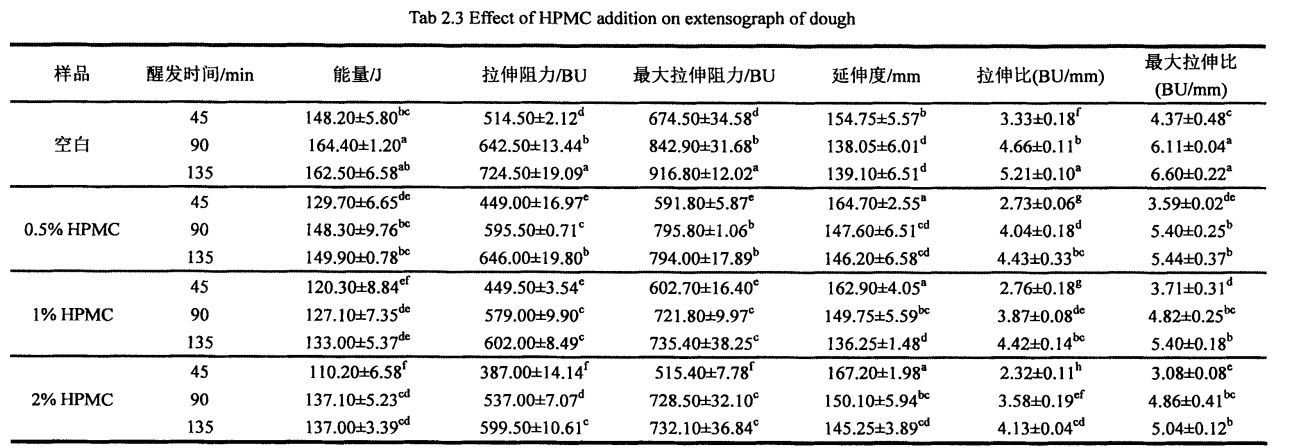
Figure 2.1 shows the change of storage modulus (elastic modulus, G') and loss modulus (viscous modulus, G") of dough with different HPMC content from 0 days to 60 days. The results showed that with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the G' of the dough without adding HPMC decreased significantly, while the change of G" was relatively small, and the /an Q (G''/G') increased. മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയ്ക്ക് ഹിമ പരവതാക്കിയാൽ കേടുപാടുകൾ സംഭവിച്ചേക്കാവുന്നതാണ്, അത് അതിന്റെ ഘടനാപരമായ ശക്തി കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു, അങ്ങനെ ഇലാസ്റ്റിക് മൊഡ്യൂളുകൾ ഗണ്യമായി കുറയുന്നു. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനയോടെ, ജി 'ന്റെ വേരിയേഷൻ ക്രമേണ കുറഞ്ഞു. In particular, when the added amount of HPMC was 2%, the variation of G' was the smallest. ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലുകളുടെ രൂപവത്കരണവും ഐസ് പരലുകളുടെ വലുപ്പത്തിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവും എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ഫലപ്രദമായി തടയാമെന്ന് ഇത് കാണിക്കുന്നു, അതുവഴി കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നാശനഷ്ടങ്ങൾ കുറയ്ക്കുകയും കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഘടനാപരമായ ശക്തി നിലനിർത്തുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. കൂടാതെ, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ജി'യുടെ മൂല്യം നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഗ്രാം (കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മൂല്യം നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമാണ്, കാരണം കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒരു വലിയ അളവിലുള്ള അന്നജം
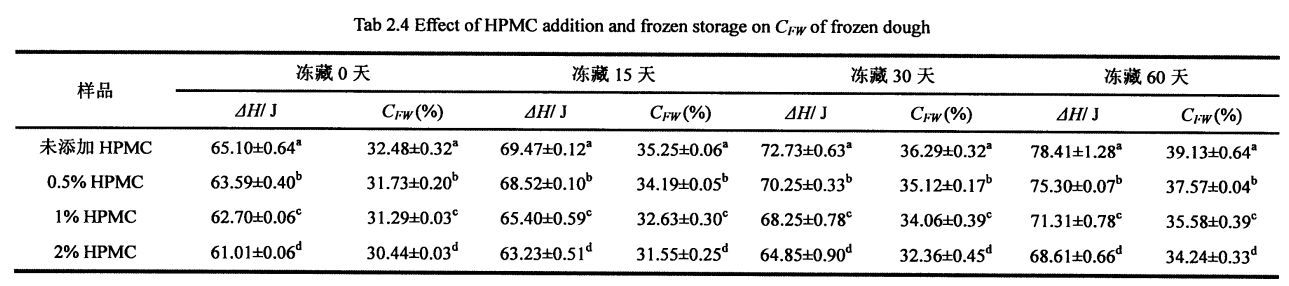
2.3.5 ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വാട്ടർ ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിൽ (7 കടയിൽ) സംഭരണ സമയം (ow) ഫലങ്ങൾ മരവിപ്പിക്കൽ സമയം മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നു
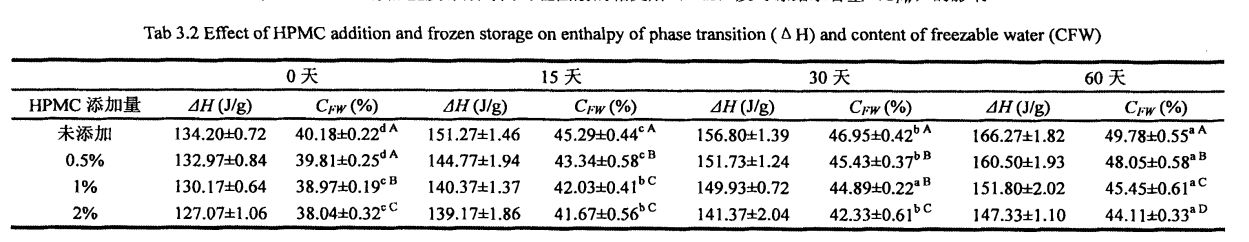
Not all the moisture in the dough can form ice crystals at a certain low temperature, which is related to the state of the moisture (free-flowing, restricted, combined with other substances, etc.) and its environment. കുറഞ്ഞ താപനിലയിൽ ഐസ് പരലുകൾ രൂപപ്പെടുത്തുന്നതിന് ഫാസ്റ്റ് പരിവർത്തനത്തിന് വിധേയമാകുന്ന കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വെള്ളമാണ് മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന വെള്ളം. മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ അളവ് ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ രൂപീകരണത്തിന്റെ എണ്ണം, വലുപ്പം, വിതരണം എന്നിവ നേരിട്ട് ബാധിക്കുന്നു. കൂടാതെ, സംഭരണ സമയത്തെ ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുന്നതിന്റെ വിപുലീകരണം, സംഭരണ താപനില എന്നിവയുടെ വിപുലീകരണം പോലുള്ള പാരിസ്ഥിതിക മാറ്റങ്ങൾ, മെറ്റീരിയൽ സിസ്റ്റം ഘടനയുടെയും ഗുണങ്ങളുടെയും മാറ്റം എന്നിവ പോലുള്ള പരിസ്ഥിതി ജലദേണും മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന ജല സംതകൾ ബാധിക്കുന്നു. For the frozen dough without added HPMC, with the prolongation of freezing storage time, Q silicon increased significantly, from 32.48±0.32% (frozen storage for 0 days) to 39.13±0.64% (frozen storage for 0 days). 60 ദിവസം ടിബറ്റൻ 20.47% ആയിരുന്നു. However, after 60 days of frozen storage, with the increase of HPMC addition, the increase rate of CFW decreased, followed by 18.41%, 13.71%, and 12.48% (Table 2.4). അതേസമയം, ഫ്രണ്ട്രോസൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 22.48 എ -0.32% മുതൽ 32.48 എ -0.32% വരെ (എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർക്കാതെ) ആയി ഉയർന്നുവന്നതുമായി കുറയുന്നു. . സംഭരണത്തിന് മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയിൽ, സംവേളമാക്കുന്നതിനൊപ്പം, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഘടന നശിപ്പിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു, അതിനാൽ മരവിപ്പിക്കാത്ത വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ ഭാഗം മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളമായി പരിവർത്തനം ചെയ്യുന്നു, അങ്ങനെ മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ അളവ് വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കും, അങ്ങനെ മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ അളവ് വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലുകളുടെ രൂപവത്കരണത്തെയും വളർച്ചയെയും hpmc- ന് ഫലപ്രദമായി തടയാനും കുഴച്ച ഘടനയുടെ സ്ഥിരത സംരക്ഷിക്കാനും കഴിയും, അതിനാൽ മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന ജലത്തിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവിനെ ഫലപ്രദമായി തടയുന്നു. ശീതീകരിച്ച നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന ജലത്തിന്റെ മാറ്റ നിയമത്തിന് ഇത് സ്ഥിരത പുലർത്തുന്നു, പക്ഷേ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ കൂടുതൽ അന്നജം അടങ്ങിയിരിക്കുന്നതിനാൽ, നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ (പട്ടിക 3.2).
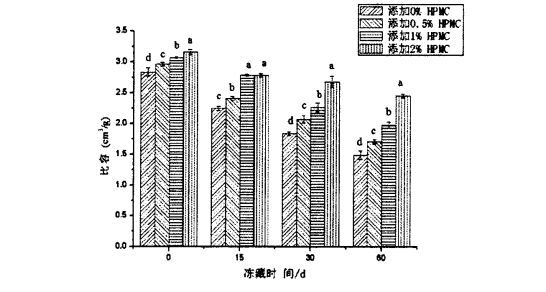
The specific volume of steamed bread can better reflect the appearance and sensory quality of steamed bread. ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച റൊട്ടിയുടെ നിർദ്ദിഷ്ട അളവ്, അതേ ഗുണനിലവാരമുള്ള ആവിയായ ബ്രെഡിന്റെ അളവ്, ഭക്ഷണത്തിന്റെ രൂപം, നിറം, ഘടന, സെൻസറി വിലയിരുത്തൽ എന്നിവയിൽ പ്രത്യേക സ്വാധീനം ചെലുത്തുന്നു. Generally speaking, steamed buns with larger specific volume are also more popular with consumers to a certain extent.
The specific volume of steamed bread can better reflect the appearance and sensory quality of steamed bread. ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച റൊട്ടിയുടെ നിർദ്ദിഷ്ട അളവ്, അതേ ഗുണനിലവാരമുള്ള ആവിയായ ബ്രെഡിന്റെ അളവ്, ഭക്ഷണത്തിന്റെ രൂപം, നിറം, ഘടന, സെൻസറി വിലയിരുത്തൽ എന്നിവയിൽ പ്രത്യേക സ്വാധീനം ചെലുത്തുന്നു. Generally speaking, steamed buns with larger specific volume are also more popular with consumers to a certain extent.
എന്നിരുന്നാലും, ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉണ്ടാക്കിയ ആവിയിൽ റൊട്ടിയുടെ നിർദ്ദിഷ്ട അളവ് ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ സമയത്തിന്റെ വിപുലീകരണം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് കുറഞ്ഞു. Among them, the specific volume of the steamed bread made from the frozen dough without adding HPMC was 2.835±0.064 cm3/g (frozen storage). 0 ദിവസം) 1.495 ± 0.070 CM3 / g വരെ (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണം); ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നിർമ്മിച്ച ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡ് 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തു 3.160 ± 0.041 CM3 / ഗ്രാം മുതൽ 2.160, ജി 3 / ജി വരെ കുറഞ്ഞു. 451±0.033 cm3/g, therefore, the specific volume of the steamed bread made from the frozen dough added with HPMC decreased with the increase of the added amount. Since the specific volume of steamed bread is not only affected by the yeast fermentation activity (fermentation gas production), the moderate gas holding capacity of the dough network structure also has an important impact on the specific volume of the final product [96'9 cited. The measurement results of the above rheological properties show that the integrity and structural strength of the dough network structure are destroyed during the freezing storage process, and the degree of damage is intensified with the extension of the freezing storage time. During the process, its gas holding capacity is poor, which in turn leads to a decrease in the specific volume of the steamed bread. However, the addition of HPMC can more effectively protect the integrity of the dough network structure, so that the air-holding properties of the dough are better maintained, therefore, in O. During the 60-day frozen storage period, with the increase of HPMC addition, the specific volume of the corresponding steamed bread decreased gradually.
2.3.6.2 ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡിന്റെ ടെക്സ്ചർ പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ സമയവും
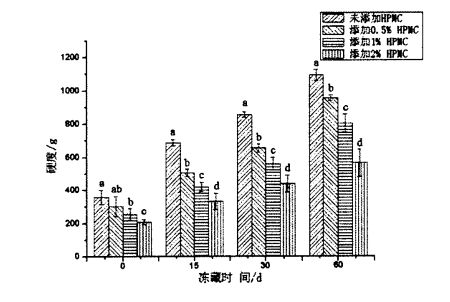
On the other hand, with the prolongation of the frozen storage time of frozen dough, the hardness of the steamed bread made by it increased significantly (P<0.05), while the elasticity decreased significantly (P<0.05). എന്നിരുന്നാലും, ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നിർമ്മിച്ച വേവിച്ച ബണ്ണുകളുടെ കാഠിന്യം 358.267 ഗ്രാം (ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സ്റ്റോറേജ് 0 ദിവസം) മുതൽ 1092.254 ഗ്രാം വരെ (64254 ഗ്രാം) ആയി ഉയർന്നു.
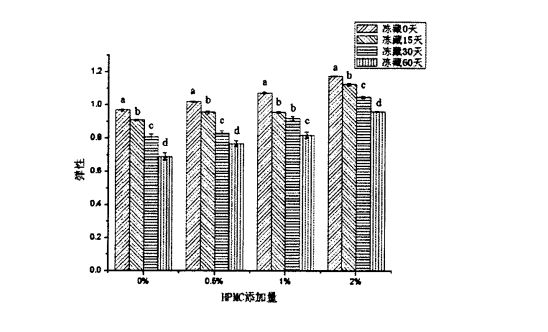
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നിർമ്മിച്ച വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡിന്റെ കാഠിന്യം 208.233 ± 15.566 ഗ്രാം (ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സ്റ്റോറേജ്) മുതൽ 564.978 വരെ) വരെ 564.978 ഗ്രാം (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രോസൺ സംഭരണം). Fig 2.4 Effect of HPMC addition and frozen storage on springiness of Chinese steamed bread In terms of elasticity, the elasticity of steamed bread made from frozen dough without adding HPMC decreased from 0.968 ± 0.006 (freezing for 0 days) to 0.689 ± 0.022 (frozen for 60 days); Frozen with 2% HPMC added the elasticity of the steamed buns made of dough decreased from 1.176 ± 0.003 (freezing for 0 days) to 0.962 ± 0.003 (freezing for 60 days). Obviously, the increase rate of hardness and the decrease rate of elasticity decreased with the increase of the added amount of HPMC in the frozen dough during the frozen storage period. ആവിയിൽ റൊട്ടിയുടെ ഗുണനിലവാരം ഫലപ്രദമായി മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്താൻ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ ഇത് കാണിക്കുന്നു. In addition, Table 2.5 lists the effects of HPMC addition and frozen storage time on other texture indexes of steamed bread. ) had no significant change (P>0.05); however, at 0 days of freezing, with the increase of HPMC addition, the Gumminess and Chewiness decreased significantly (P
On the other hand, with the prolongation of freezing time, the cohesion and restoring force of steamed bread decreased significantly. For steamed bread made from frozen dough without adding HPMC, its cohesion was increased by O. 86-4-0.03 g (frozen storage 0 days) was reduced to 0.49+0.06 g (frozen storage for 60 days), while the restoring force was reduced from 0.48+0.04 g (frozen storage for 0 days) to 0.17±0.01 (frozen storage for 0 days) 60 days); however, for steamed buns made from frozen dough with 2% HPMC added, the cohesion was reduced from 0.93+0.02 g (0 days frozen) to 0.61+0.07 g (frozen storage for 60 days), while the restoring force was reduced from 0.53+0.01 g (frozen storage for 0 days) to 0.27+4-0.02 (frozen storage for 60 days). In addition, with the prolongation of frozen storage time, the stickiness and chewiness of steamed bread increased significantly. എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർക്കാതെ ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഉണ്ടാക്കിയ ആവിയിൽ റൊട്ടി, സ്റ്റിക്കിനെ 336.54 + 37 വർദ്ധിപ്പിച്ചു. 24 (0 days of frozen storage) increased to 1232.86±67.67 (60 days of frozen storage), while chewiness increased from 325.76+34.64 (0 days of frozen storage) to 1005.83+83.95 (frozen for 60 days); however, for the steamed buns made from frozen dough with 2% HPMC added, the stickiness increased from 206.62+1 1.84 (frozen for 0 days) to 472.84. 96+45.58 (frozen storage for 60 days), while chewiness increased from 200.78+10.21 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 404.53+31.26 (frozen storage for 60 days). സംഭരണം മൂലമുണ്ടാകുന്ന ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച ബ്രെഡിന്റെ ഘടകത്തിലെ മാറ്റങ്ങളെ തടസ്സപ്പെടുത്തുമെന്ന് ഇത് കാണിക്കുന്നു. In addition, the changes in the texture properties of steamed bread caused by freezing storage (such as the increase of stickiness and chewiness and the decrease of recovery force) There is also a certain internal correlation with the change of steamed bread specific volume. Thus, dough properties (eg, farinality, elongation, and rheological properties) can be improved by adding HPMC to frozen dough, and HPMC inhibits the formation, growth, and redistribution of ice crystals (recrystallization process), making frozen dough The quality of the processed steamed buns is improved.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a kind of hydrophilic colloid, and its application research in frozen dough with Chinese-style pasta food (such as steamed bread) as the final product is still lacking. The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of HPMC improvement by investigating the effect of HPMC addition on the processing properties of frozen dough and the quality of steamed bread, so as to provide some theoretical support for the application of HPMC in steamed bread and other Chinese-style flour products. The results show that HPMC can improve the farinaceous properties of the dough. When the addition amount of HPMC is 2%, the water absorption rate of the dough increases from 58.10% in the control group to 60.60%; 2 min increased to 12.2 min; at the same time, the dough formation time decreased from 2.1 min in the control group to 1.5 mill; the weakening degree decreased from 55 FU in the control group to 18 FU. In addition, HPMC also improved the tensile properties of the dough. With the increase in the amount of HPMC added, the elongation of the dough increased significantly; ഗണ്യമായി കുറഞ്ഞു. കൂടാതെ, ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ കാലയളവിൽ, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മൂലമുണ്ടാകുന്ന ജലത്തിന്റെ വർദ്ധിച്ച നിരക്ക്, അതുവഴി കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വിസ്കോലറ്റിറ്റിയുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ശേഷിയും നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയുടെ സമഗ്രതയും നിലനിർത്തുന്നു. അന്തിമ ഉൽപ്പന്നത്തിന്റെ ഗുണനിലവാരം ഉറപ്പുനൽകുന്നു.
On the other hand, the experimental results showed that the addition of HPMC also had a good quality control and improvement effect on steamed bread made from frozen dough. ഏകീകൃത സാമ്പിളുകൾക്കായി, ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച അപ്പത്തിന്റെ നിർദ്ദിഷ്ട അളവ് വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുകയും ആവിയിൽ അപ്പം വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുകയും ചെയ്തു - അതേ സമയം ആവിയിൽ വേവിച്ച അപ്പം വർദ്ധിപ്പിച്ചു. In addition, the addition of HPMC inhibited the deterioration of the quality of steamed buns made from frozen dough with the extension of freezing storage time - reducing the degree of increase in the hardness, stickiness and chewiness of the steamed buns, as well as reducing the elasticity of the steamed buns, Cohesion and recovery force decrease.
അധ്യായം 3 ഫ്രീസിംഗ് അവസ്ഥകളിൽ ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂട്ടന്റെ ഘടനയിലും സവിശേഷതകളിലും എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ
3.1 ആമുഖം
Wheat gluten is the most abundant storage protein in wheat grains, accounting for more than 80% of the total protein. അതിന്റെ ഘടകങ്ങളുടെ ലായകതാമനുസരിച്ച്, ഇത് ഗ്ലൂട്ടിൻ ഭാഷയിലേക്ക് തിരിക്കാം (ക്ഷാര ലായനിയിൽ ലയിക്കുന്നതും ഗ്ലിയാഡിൻ (ക്ഷാര പരിഹാരത്തിൽ). in ethanol solution). അവയിൽ, ഗ്ലൂട്ടോനിന്റെ തന്മാത്രാ ഭാരം (എംഡബ്ല്യു) 1x107da വരെ ഉയർന്നതാണ്, ഇതിന് രണ്ട് സുഫുനിറ്റുകളുണ്ട്, അത് ഇന്റർമോളിക്യുലാർ, ഇൻട്രാമോളിക്യുലർ ഡൈൾഫൈഡ് ബോണ്ടുകളുണ്ട്; ഗ്ലിയാഡിനിന്റെ തന്മാത്രാ ഭാരം 1x104DA മാത്രമാണെങ്കിലും ഒരു സുസൂനിന് മാത്രമേയുള്ളൂ, അത് ഒരു സുസൂനിന് മാത്രമേയുള്ളൂ, അത് തന്മാത്രകളെ ആന്തരിക തികഞ്ഞ ബോണ്ട് രൂപീകരിക്കാൻ കഴിയും. Campos, Steffe, & Ng (1 996) divided the formation of dough into two processes: energy input (mixing process with dough) and protein association (formation of dough network structure). കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ രൂപവനുസരിച്ച് ഗ്ലൂട്ടോനിൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഇലാസ്തികത, ഘടനാപരമായ ശക്തി എന്നിവ നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നു, അതേസമയം ഗ്ലിയാഡിൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വിസ്കോസിറ്റി, ഇൻക്ലൂതത എന്നിവ നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നു. കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയുടെ രൂപവത്കരണത്തിൽ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന് ഒഴിച്ചുകൂടാനാവാത്തതും അതുല്യവുമായ പങ്കിനെക്കുറിച്ച് കാണാം, ഒപ്പം കോഹെഷനും വിസ്കോലലാസ്റ്റിറ്റിയും ജലചിതിയും ഉപയോഗിച്ച് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ അവസാനിപ്പിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
In addition, from a microscopic point of view, the formation of the three-dimensional network structure of dough is accompanied by the formation of intermolecular and intramolecular covalent bonds (such as disulfide bonds) and non-covalent bonds (such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic forces) [103]. ദ്വിതീയ ബോണ്ടിന്റെ energy ർജ്ജം ആണെങ്കിലും
അളവും സ്ഥിരതയും കോവാലന്റ് ബോണ്ടുകളേക്കാൾ ദുർബലമാണ്, പക്ഷേ ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ അനുരൂപമാക്കുന്നതിൽ അവർ ഒരു പ്രധാന പങ്ക് വഹിക്കുന്നു [1041].
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സാഹചര്യങ്ങൾ, ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലുകൾ (ക്രിസ്റ്റലൈസേഷൻ, റെക്രിമാൾഎസേഷൻ പ്രക്രിയ) എന്നിവയുടെ രൂപവത്കരണവും വളർച്ചയും കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയെ ശാരീരികമായി ഞെക്കിപ്പിടിക്കും, അതിന്റെ ഘടനാപരമായ സമഗ്രത നശിപ്പിക്കും, മൈക്രോസ്കോപ്പിക്കലായി. ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ഘടനയുടെയും സ്വഭാവത്തിലും മാറ്റങ്ങൾക്കൊപ്പം [105'1061. ഷാവോ എന്ന നിലയിൽ എട്ട് എ 1. . കൂടാതെ, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ സ്പേഷ്യൽ അനുരൂപമായ മാറ്റങ്ങളും തെർമോഡൈനാനാമിക് ഗുണങ്ങളും കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് ഗുണങ്ങളെയും ഉൽപ്പന്ന നിലവാരത്തെയും ബാധിക്കും. Therefore, in the process of freezing storage, it is of certain research significance to investigate the changes of water state (ice crystal state) and the structure and properties of gluten protein under different freezing storage time conditions.
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒരു സെല്ലുലോസ് ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് ഹൈഡ്രോകോൾലോയിഡ് (എച്ച്പിഎംസി) പ്രയോഗിച്ചതുപോലെ, ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഹൈഡ്രോക്സിപ്രോപൈൽ മെത്തിൽസെല്ലുലോസ് പ്രയോഗിക്കുന്നു, അതിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തന സംവിധാനത്തെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ഗവേഷണങ്ങൾ പോലും കുറവാണ്.
3.2.1 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കൾ
ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ അൻഹു റൂ സിയാങ് ഫു സിയാങ് ഫുഡ് കോ., ലിമിറ്റഡ്.; ഹൈഡ്രോക്സിപ്രോപൈൽ മെത്തിൽസെല്ലുലോസ് (എച്ച്പിഎംസി, മുകളിൽ പറഞ്ഞതുപോലെ) അലഡിൻ രാസ ഏജന്റ് കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
3.2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഉപകരണം
ഉപകരണങ്ങളുടെ പേര്
കണ്ടെത്തൽ. R3 RAROMETER
Dsc. Q200 ഡിഫറൻഷ്യൽ സ്കാൻ ചെയ്യുന്നത് കലോറിമീറ്റർ
PQ00 1 കുറഞ്ഞ ഫീൽഡ് എൻഎംആർ ഉപകരണം
722E സ്പെക്ട്രോഫോട്ടോമീറ്റർ
ജെഎസ്എം. 6490LV Tungsten Filament Scanning Electron Microscope
HH ഡിജിറ്റൽ നിരന്തരമായ താപനില വാട്ടർ ബാത്ത്
ബിസിഡി. 201LCTST റഫ്രിജറേറ്റർ
ഞാൻ. 5 അൾട്രാ-മൈക്രോ ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് ബാലൻസ്
ഓട്ടോമാറ്റിക് മൈക്രോപ്ലേറ്റ് റീഡർ
നിക്കോലെറ്റ് 67 ഫോറിയർ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രോമീറ്റർ
കെഡിസി. 160 മണിക്കൂർ അതിവേഗ ശീതീകരിച്ച സെൻട്രിഫ്യൂജ്
Mx. S type eddy current oscillator
Sx2.4.10 മഫിൽ ചൂള
കെജെഇറ്റ്ക് ടിഎം 8400 ഓട്ടോമാറ്റിക് കെജെൽഡഹാൽ നൈട്രജൻ അനലൈസർ
നിര്മ്മാതാവ്
അമേരിക്കൻ ടിഎ കമ്പനി
അമേരിക്കൻ ടിഎ കമ്പനി
ഷാങ്ഹായ് സ്പെക്ട്രം ഇൻസ്ട്രുമെന്റ് കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ഹെഫെ മെയി ലിംഗ് കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
സാർട്ടോറിയസ്, ജർമ്മനി
തെർമോ ഫിഷർ, യുഎസ്എ
അനസ് സോങ് കെഹോംഗ് ജിയ സയന്റിഫിക് ഇൻസ്ട്രാ യൂണിറ്റിക്
തെർമോ ഫിഷർ, യുഎസ്എ
ഹുവാങ്ഷി ഹെങ്ഫെങ് മെഡിക്കൽ ഉപകരണ കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
3.2.3 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക പ്രതിരോധം
പരീക്ഷണങ്ങളിൽ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന എല്ലാ രാസ റിയാക്ടറുകളും അനലിറ്റിക്കൽ ഗ്രേഡായിരുന്നു.
3.2.4.1 ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ അടിസ്ഥാന ഘടകങ്ങളുടെ നിർണ്ണയം
ജിബി 5009.5_2010, ജിബി 50094.2010, ജിബി 5009.6.20030, ജിബി 5009.6.2003T78-81, ഗ്ലൂറ്റനിൽ ഉള്ളടക്കം, ഗ്ലൂറ്റനിൽ ഉള്ളടക്കം
3.2.4.2 ഫ്രോസൺ വെറ്റ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ (ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ)
ഒരു ബേക്കറിൽ 100 ഗ്രാം ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ (40%, w / w) ചേർക്കുക, 5 മിനിറ്റ് ഒരു ഗ്ലാസ് വടി ചേർത്ത്, ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിൽ അത് മരവിപ്പിക്കുക .18 to എന്നത് ഒരു പ്രത്യേക കാലയളവിൽ വയ്ക്കുക. of time (15 days, 30 days and 60 days). Take the frozen 0-day sample (je, fresh unfrozen wet gluten mass) as the blank control group. Use 0.5%, 1% and 2% HPMC (w/w) to replace the corresponding quality of gluten Prion powder, and the rest of the production steps and freezing treatment remain unchanged, so as to prepare wet gluten dough samples with different HPMC additions.
Frequency sweep, the specific experimental parameters are set as follows - the strain is 0.5% (at LVR), and the frequency sweep range is 0.1 Hz. 10 Hz, while other parameters are the same as the strain sweep parameters. Scanning data is acquired in logarithmic mode, and 5 data points (plots) are recorded in the rheological curve for every 10-fold increase in frequency, so as to obtain the frequency as the abscissa, the storage modulus (G') and the loss modulus (G') is the rheological discrete curve of the ordinate. It is worth noting that after each time the sample is pressed by the clamp, the excess sample needs to be gently scraped with a blade, and a layer of paraffin oil is applied to the edge of the sample to prevent moisture during the experiment. of loss. ഓരോ സാമ്പിളിലും മൂന്ന് തവണ പകർത്തി.
3.2.4.4 തെർമോഡൈനാമിക് പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികളുടെ നിർണ്ണയം
സാമ്പിളുകളുടെ പ്രസക്തമായ തെർമോഡൈനാനാമിക് ഗുണങ്ങൾ അളക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഈ പരീക്ഷണത്തിൽ ബോട്ട് (2003) രീതി അനുസരിച്ച് (ഡിഎസ്സി ക്യു.2 ണ്ട്) ഈ പരീക്ഷയിൽ ഉപയോഗിച്ചു.
നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂട്ടന്റെ 15 മില്ലിഗ്രാം സാമ്പിൾ തൂക്കമുണ്ടാക്കി (ദ്രാവക സാമ്പിളുകൾക്ക് അനുയോജ്യം). The determination procedure and parameters are as follows: equilibrate at 20°C for 5 min, then drop to .30°C at a rate of 10°C/min, keep the temperature for 10 min, and finally increase to 25°C at a rate of 5°C/min, purge the gas (Purge Gas) was nitrogen (N2) and its flow rate was 50 mL/min, and a blank sealed aluminum crucible was used as a reference. The obtained DSC curve was analyzed using the analysis software Universal Analysis 2000, by analyzing the peaks located around 0 °C. Integral to get the melting enthalpy of ice crystals (Yu day). Then, the freezable water content (CFW) is calculated by the following formula [85-86]:
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത വരണ്ട, ശീതീകരിച്ച-സംഭരണ സംസ്കരിച്ച സാമ്പിൾ, അത് വീണ്ടും പൊടിക്കുക, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ പൊടി ലഭിക്കാൻ 100 മെഷ് അരിപ്രയിലൂടെ കടന്നുപോകുക (ഈ ദൃ solid മായ പൊടി സാമ്പിൾ 2.8 ന് ബാധകമാണ്). 10 മില്ലിഗ്രാം ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ സാമ്പിൾ തൂക്കമുണ്ടാക്കുകയും ഒരു അലുമിനിയം ക്രൂസിയറിൽ അടയ്ക്കുകയും ചെയ്തു (കട്ടിയുള്ള സാമ്പിളുകൾക്കായി). ഡിഎസ്സി അളവെടുപ്പ് പാരാമീറ്ററുകൾ ഇപ്രകാരമായി സജ്ജമാക്കി, 5 മിനിറ്റ് 20 ° C എന്ന നിലയിൽ 5 ° C ആയി ഉയർത്തി, തുടർന്ന് നൈട്രജൻ ശുദ്ധഗമരീതി 80 മില്ലിഗ്രാം ആയി ഉയർന്നു, അതിന്റെ ഒഴുക്ക് നിരക്ക് 80 മില്ലിഗ്രാം. Using a sealed empty crucible as a reference, and use the analysis software Universal Analysis 2000 to analyze the obtained DSC curve to obtain the peak temperature of thermal denaturation of wheat gluten protein (Yes). Each sample is replicated three times.
The content of free sulfhydryl groups was determined according to the method of Beveridg, Toma, & Nakai (1974) [Hu], with appropriate modifications. 40 മില്ലിഗ്രാം ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ സാമ്പിൾ, നന്നായി കുലുക്കുക, ഇത് 4 മില്ലി ഡോഡെസിൽ സൾഫോണേറ്റിൽ വിതറി
Sodium Sodium (SDS). ട്രിസ്-ഹൈഡ്രോക്സിമെഥൈൽ അമിനോമെതൻ (ട്രിസ്). ഗ്ലൈസിൻ (ഗ്ലൈ). ടെറ്റ്റെസിറ്റിക് ആസിഡ് 7, അമൈൻ (എഡിറ്റ്) ബഫർ (10.4% ട്രിസ്, 6.9 ഗ്രാം ഗ്ലൈസിൻ, 1.2 ജി എട്റ്റ / എൽ, പിഎച്ച് 8.0, ഇത് 30 മിനിറ്റ് നേരത്തേക്ക് ചേർത്തു. തുടർന്ന്, ഓരോ 10 മിനിറ്റിലും ഇത് ചേർത്തു. 4 ° C ന് 10 മിനിറ്റ്, 5000 × ജി. ആദ്യം, അത്യോമാസി മിശ്രദ്ധ നീല (ജി.2.20) രീതി (അത്രോബെൻസോയിക് ആസിഡ്, 30 മിനിറ്റ് കഴിഞ്ഞ് 4 റാഗ് / മിൻ) in a 25 ℃ water bath, add 412 nm absorbance, and the above buffer was used as blank control. Finally, the free sulfhydryl content was calculated according to the following formula:
അവരിൽ 73.53 ആണ് വംശനാശപരമായ ഗുണകം; A ആണ് ആഗിരണം D ആണ് നിരാകരണ ഘടകം (ഇവിടെ 1); G എന്നത് പ്രോട്ടീൻ ഏകാഗ്രതയാണ്. Each sample was replicated three times.
കോണ്ടാഡിയർഗോസ് അനുസരിച്ച്, ഗോഫ്, കസപിസ് (2007) രീതി [1111, 2 ഗ്രാം വ്യാസമുള്ള പിണ്ഡം 10 മില്ലീറ്റൽ മാഗ്നിറ്റിക് ട്യൂബ് സ്ഥാപിച്ചു, തുടർന്ന് തിരശ്ചീന റാപ് ഉപയോഗിച്ച് അടച്ചിട്ട്, തുടർന്ന് 3 മിനിറ്റ് ഇഫൈലിബ്രിയറ്റ്, ഫീൽഡ് സ്ഫൈൻ 0.43 ടി, അനുരണന ആവൃത്തി 18.169 HZ ആണ്, കൂടാതെ, പൾസ് സീക്വൻസ് യഥാക്രമം 900, 1 800 എന്നീ നിലകൾ യഥാക്രമം 13 നും 1 800 ഉം ആണ്, കൂടാതെ അപചയ വക്രത്തിന്റെ ഇടപെടലും വ്യാപനവും കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിനും പൾസ് ഇടവേള r. In this experiment, it was set to O. 5 m s. ഓരോ സ്കാൻവും തമ്മിലുള്ള 1 എസ് ഇടവേള ഉപയോഗിച്ച് സിഗ്നൽ-ടു-നോയ്സ് അനുപാതം (എസ്എൻആർ) വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന് ഓരോ അസയയും 8 തവണ സ്കാൻ ചെയ്തു. The relaxation time is obtained from the following integral equation:
സ്വതന്ത്ര വേരിയബിളായി സമയമുള്ള സിഗ്നൽ വ്യാപ്തിയുടെ എക്സ്പോണൻഷ്യൽ ക്ഷയത്തിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തനത്തിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തനമാണ് അവ. Yang) is the function of the hydrogen proton number density with the relaxation time (D) as the independent variable.
പ്രൊവിഷ്സ്റ്റർ വിശകലന സോഫ്റ്റ്വെയറിൽ പ്രോവെൻച്ചർ വിശകലന സോഫ്റ്റ്വെയറിൽ സംയോജിപ്പിച്ച്, ലാപ്റ്റിൻ ഇൻവെർപ്പ് പരിവർത്തനവുമായി സംയോജിപ്പിച്ച്, തുടർച്ചയായ വിതരണ വക്ര ലഭിക്കുന്നതിന് വിപരീത പ്രകടനം നടത്തുന്നു. Each sample was repeated three times
ഈ പരീക്ഷണത്തിൽ, ഒരു ഫോറയർ ട്രാൻസ്ഫർ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രോമീറ്റൽ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ദ്വിതീയ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടന നിർണ്ണയിക്കാൻ മൊത്തം പ്രതിഫലന (എടിആർ) ആക്സസറി ഉപയോഗിച്ചു, ഒരു കാഡ്മിയം മെർക്കുറി ടെല്ലുറൈഡ് ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ ഡിറ്റക്ടറായി ഉപയോഗിച്ചു. സാമ്പിളിനും പശ്ചാത്തല ശേഖരണത്തെയും 4 സെന്റിമീറ്റർ റെസല്യൂഷനോടെ 64 തവണ സ്കാൻ ചെയ്തു ~ കൂടാതെ 4000 CMQ-500 സെന്റിമീറ്ററും സ്കാനിംഗ് ശ്രേണി. ആട്രിക്റ്റിംഗിലെ ഡയമണ്ടിന്റെ ഉപരിതലത്തിൽ ഒരു ചെറിയ അളവിൽ പ്രോട്ടീൻ സോളിൻ പൊടി പരത്തുക, തുടർന്ന്, 3 ഓൾ ഘടികാരദിശയിൽ, ഒടുവിൽ നിങ്ങൾ സാമ്പിളിന്റെ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രം സിഗ്നൽ ശേഖരിക്കാൻ തുടങ്ങും, ഒടുവിൽ അബ്സീനമ്പർ, സെ.മീ. (Absorption) is the infrared spectrum of the ordinate.
ലഭിച്ച പൂർണ്ണ വേവെനമ്പർ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രത്തിൽ ഓട്ടോമാറ്റിക് ബേസ്ലൈൻ തിരുത്തലും അഡ്വാൻസ്ഡ് എടിആർ തിരുത്തലും നടത്താൻ ഓമ്നിക് സോഫ്റ്റ്വെയർ ഉപയോഗിക്കുക, തുടർന്ന് കൊടുമുടി ഉപയോഗിക്കുക. ഫിറ്റ് 4.12 സോഫ്റ്റ്വെയർ ബേസ്ലൈൻ തിരുത്തൽ, നാലിൻറെ അപകർഷതാവസ്ഥ, അമിത് III ബാൻഡിലെ 09 അല്ലെങ്കിൽ അതിൽ കൂടുതൽ ഫിറ്റിംഗ് എന്നിവ (1350 സെക്കൻഡിമീറ്റർ --11200 സെക്കൻഡറിന് യോജിക്കുന്നു), ഓരോ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയ്ക്കും ശേഷമുള്ള സംയോജിത പീക്ക് ഏരിയയും ഒടുവിൽ ലഭിക്കുന്നു, ഒപ്പം ഓരോ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയ്ക്കും അനുസൃതമായി, ഓരോ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയുടെയും ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കം കണക്കാക്കുന്നു. തുക (%), അതായത്, പീക്ക് ഏരിയ / മൊത്തം പീക്ക് ഏരിയ. Three parallels were performed for each sample.
3.2.4.8 ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ഉപരിതല ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിസിറ്റി നിർണ്ണയിക്കുക
കാറ്റോ & നകായ് (1980) രീതി അനുസരിച്ച് [1180) [112], ഗോതമ്പ് ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ ഉപരിതലത്തിന്റെ ഉപരിതല നിർണ്ണയിക്കാൻ ഒരു ഫ്ലൂറസെന്റ് അന്വേഷണായി (എ ഉത്തരം. 100 മില്ലിഗ്രാം ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ സോളിൻ സോളിൻ സോളിൻ പവർ സാമ്പിൾ, 0.2 മി, പിഎച്ച്പിഎം, പി.എസ്.എം.എസ്.. അളക്കൽ ഫലങ്ങൾ അനുസരിച്ച്, അമാനുഷികത 5 ഏകാഗ്രത ഗ്രേഡിയന്റുകൾക്കായി പിബിഎസ് ഉപയോഗിച്ച് ലയിപ്പിക്കുന്നു, പ്രോട്ടീൻ ഏകാഗ്രത 0 .02.0.5 മില്ലിഗ്രാം / എംഎൽ റേഞ്ച്.
After freeze-drying the wet gluten mass without adding HPMC and adding 2% HPMC that had been frozen for 0 days and 60 days, some samples were cut out, sprayed with gold 90 S with an electron sputter, and then placed in a scanning electron microscope (JSM.6490LV). മോർഫോളജിക്കൽ നിരീക്ഷണം നടത്തി. The accelerating voltage was set to 20 KV and the magnification was 100 times.
എല്ലാ ഫലങ്ങളും 4-സ്റ്റാൻഡേർഡ് ഡീവിയേഷനായി പ്രകടിപ്പിക്കുന്നു, ഇലക്ട്രോൺ മൈക്രോസ്കോപ്പി സ്കാനിംഗ് ചെയ്യുന്നതല്ലാതെ മുകളിലുള്ള പരീക്ഷണങ്ങൾ കുറഞ്ഞത് മൂന്ന് തവണ ആവർത്തിച്ചു. ചാർട്ടുകൾ വരയ്ക്കുന്നതിനും എസ്പിഎസ്എസ് 19.0 ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നതിനും ഉത്ഭവം 8.0 ഉപയോഗിക്കുക. വേരിയൻസ്, ഡങ്കന്റെ ഒന്നിലധികം ശ്രേണി ടെസ്റ്റ് എന്നിവയുടെ വേ വിശകലനം 0.05 ആയിരുന്നു.
3. ഫലങ്ങളും ചർച്ചയും
3.3.1 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പിണ്ഡത്തിന്റെ വാഞ്ഞുകയെടുക്കുന്ന സംഭരണ സമയത്തെ മരവിപ്പിക്കുക
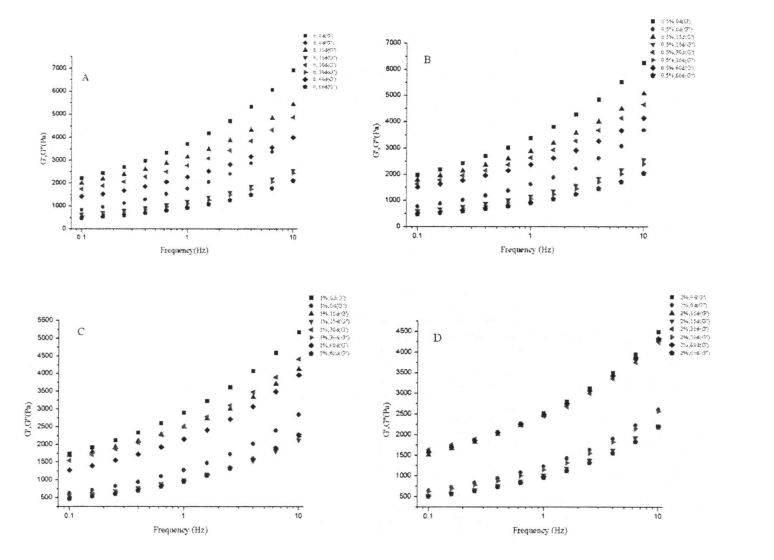
FIG 3.1 ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വാളായി റിയോളജിക്കൽ ഗുണങ്ങളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണവും
കുറിപ്പ്: എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർക്കാതെ നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ ആന്ദാസവകാശ ഫലം അവയ്ക്കിടയിലാണ്: ബി എന്നത് നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ ആറ്റെടുക്കൽ സ്കാനിംഗ് ഫലമാണ് 0.5% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർക്കുന്നത്; സി ആണ് 1% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ആന്ദോവധ്യം: ഡി ആണ് 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി നനഞ്ഞ ആന്ദോളേഷൻ ആവൃത്തിയുടെ ആവൃത്തിയുടെ ആവൃത്തി ഫലങ്ങൾ ചേർക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ആന്ദോവധ്യം.
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യൽ പോയിന്റിന് താഴെ താപനിലയിൽ മരവിപ്പിക്കാവുന്ന വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ ഘട്ട മാറ്റത്തിലൂടെ ഐസ് പരലുകൾ രൂപപ്പെടുന്നു. Therefore, the content of freezable water directly affects the number, size and distribution of ice crystals in the frozen dough. The experimental results (Table 3.2) show that as the freezing storage time is extended from 0 days to 60 days, the wet gluten mass Chinese silicon gradually becomes larger, which is consistent with the research results of others [117'11 81]. In particular, after 60 days of frozen storage, the phase transition enthalpy (day) of the wet gluten mass without HPMC increased from 134.20 J/g (0 d) to 166.27 J/g (60 d), that is, the increase increased by 23.90%, while the freezable moisture content (CF silicon) increased from 40.08% to 49.78%, an increase of 19.59%. However, for the samples supplemented with 0.5%, 1% and 2% HPMC, after 60 days of freezing, the C-chat increased by 20.07%, 16, 63% and 15.96%, respectively, which is consistent with Matuda, et a1. (2008) found that the melting enthalpy (Y) of the samples with added hydrophilic colloids decreased compared with the blank samples [119].
3.3.2.2 ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ താപ സ്ഥിരതയിൽ നിന്ന് എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഉള്ളടക്കവും സംഭരണ സമയവും ചേർക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ
തെർമലി പ്രോസസ്സ് ചെയ്ത പാസ്തയുടെ ധാന്യ രൂപവത്കരണത്തിലും ഉൽപ്പന്ന നിലവാരത്തിലും ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ താപ സ്ഥിരതയ്ക്ക് ഒരു പ്രധാന സ്വാധീനമുണ്ട് [211]. ക്രിബ്ലികളായി അബ്സസ്സ, ചൂട് ഒഴുക്ക് (മെഗ്) എന്ന താപനില (° C) എന്ന താപനില (° C) എന്ന താപനില (° C) ചിത്രം 3.2 കാണിക്കുന്നു. The experimental results (Table 3.3) found that the heat denaturation temperature of gluten protein without freezing and without adding I-IPMC was 52.95 °C, which was consistent with Leon, et a1. (2003) ഖർകർ, ബരാക്, മുഡ്ഗൈൽ (2013) വളരെ സമാനമായ ഫലങ്ങൾ റിപ്പോർട്ട് ചെയ്തു [120M11. With the addition of 0% unfrozen, O. Compared with the heat denaturation temperature of gluten protein with 5%, 1% and 2% HPMC, the heat deformation temperature of gluten protein corresponding to 60 days increased by 7.40℃, 6.15℃, 5.02℃ and 4.58℃, respectively. Obviously, under the condition of the same freezing storage time, the increase of denaturation peak temperature (N) decreased sequentially with the increase of HPMC addition. This is consistent with the change rule of the results of Cry. In addition, for the unfrozen samples, as the amount of HPMC added increases, the N values decrease sequentially. This may be due to the intermolecular interactions between HPMC with molecular surface activity and gluten, such as the formation of covalent and non-covalent bonds [122J].
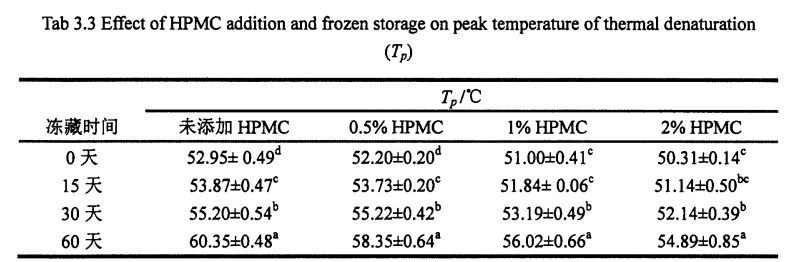
കുറിപ്പ്: വ്യത്യസ്ത Superscript ഒരേ നിരയിലെ ചെറിയ അക്ഷരങ്ങൾ സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു (പേജ് <0.05) കൂടാതെ, പ്രോട്ടീൻ തന്മാത്ര കൂടുതൽ ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ തുറന്നുകാണിക്കുകയും തന്മാത്രയുടെ ഡിനാറ്ററേഷൻ പ്രക്രിയയിൽ പങ്കെടുക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നുവെന്ന് മിതീയർ (1990) വിശ്വസിച്ചു [1231]. അതിനാൽ, ഗ്ലൂറ്റനിലെ കൂടുതൽ ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിനിടയിൽ തുറന്നുകാട്ടി, ഒപ്പം എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ അനുയായികൾ ഫലപ്രദമായി സ്ഥിരത പുലർത്താൻ കഴിയും.
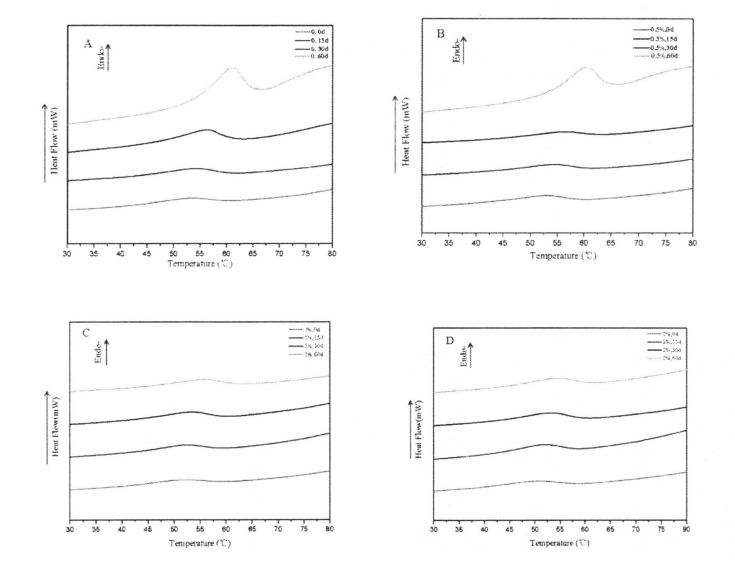
Fig 3.2 Typical DSC thermograms of gluten proteins with 0%HPMC(A);with O.5%HPMC(B); with 1%HPMC(C);with 2%HPMC(D)after different time of frozen storage,from 0d to 60d indicated from the lowest curve to the highest one in each graph. Note: A is the DSC curve of wheat gluten without adding HPMC; B is the addition of O. DSC curve of wheat gluten with 5% HPMC; C is the DSC curve of wheat gluten with 1% HPMC; D is the DSC curve of wheat gluten with 2% HPMC 3.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing time on free sulfhydryl content (C-SH) Intermolecular and intramolecular covalent bonds are very important for the stability of dough network structure. A disulfide bond (-SS-) is a covalent linkage formed by dehydrogenation of two free sulfhydryl groups (.SH). Glutenin is composed of glutenin and gliadin, the former can form intramolecular and intermolecular disulfide bonds, while the latter can only form intramolecular disulfide bonds [1241] Therefore, disulfide bonds are an intramolecular/intermolecular disulfide bond. ക്രോസ്-ലിങ്കിംഗിന്റെ പ്രധാന മാർഗം. Compared to adding 0%, O. The C-SH of 5% and 1% HPMC without freezing treatment and the C-SH of gluten after 60 days of freezing have different degrees of increase respectively. Specifically, the face with no HPMC added gluten C. SH increased by 3.74 "mol/g to 8.25 "mol/g, while C.sh, shellfish, with gluten supplemented with 0.5% and 1% HPMC increased by 2.76 "mol/g to 7.25""mol/g and 1.33 "mol/g to 5.66 "mol/g (Fig. 3.3). Zhao, et a1. (2012) found that after 120 days of frozen storage, the content of free thiol groups increased significantly [ 1071. It is worth noting that the C-SH of gluten protein was significantly lower than that of other frozen storage periods when the freezing period was 15 days, which may be attributed to the freezing shrinkage effect of gluten protein structure, which makes the More intermolecular and intramolecular disulfide bonds were locally formed in a shorter freezing time [1161. Wang, et a1. (2014) found that the C-SH of glutenin-rich proteins was also significantly increased after 15 days of freezing. Decreased [1251. However, the gluten protein supplemented with 2% HPMC did not increase significantly except for C-SH, which also decreased significantly at 15 days, with the extension of freezing time.
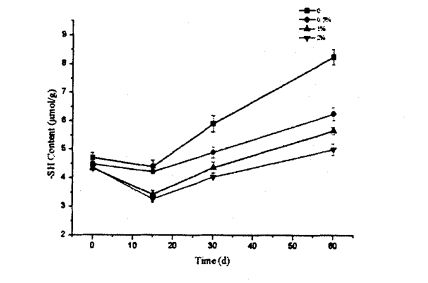
Fig 3.3 Effect of HPMC addition and frozen storage on the content of free-SH for gluten proteins As mentioned above, freezable water can form ice crystals at low temperatures and distribute in the interstices of the gluten network. Therefore, with the prolongation of freezing time, the ice crystals become larger, which squeezes the gluten protein structure more seriously, and leads to the breakage of some intermolecular and intramolecular disulfide bonds, which increases the content of free sulfhydryl groups. On the other hand, the experimental results show that HPMC can protect the disulfide bond from the extrusion damage of ice crystals, thereby inhibiting the depolymerization process of gluten protein. 3.3.4 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ, വിശാലമായ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പിണ്ഡത്തിന്റെ (ടി 2) Figure 3.4 shows the distribution of wet gluten mass at 0 and 60 days with different HPMC additions, including 4 main distribution intervals, namely 0.1.1 ms (T21), 1.10 ms (T22), 10.100 ms (dead;) and 1 00-1 000 ms (T24). ബോസ്മാൻ മറ്റുള്ളവരും. (2012) found a similar distribution of wet gluten mass [1261], and they suggested that protons with relaxation times below 10 ms could be classified as rapidly relaxing protons, which are mainly derived from poor mobility the bound water, therefore, may characterize the relaxation time distribution of bound water bound to a small amount of starch, while Dang may characterize the relaxation time distribution of bound water bound to gluten protein. In addition, Kontogiorgos (2007) - t11¨, the "strands" of the gluten protein network structure are composed of several layers (Sheets) about 5 nm apart, and the water contained in these layers is limited water (or Bulk water, phase water), the mobility of this water is between the mobility of bound water and free water. നിയന്ത്രിത വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ വിശ്രമ സമയ വിതരണമാണ് ടി 223 ആട്രിബ്യൂട്ട് ചെയ്യാം. The T24 distribution (>100 ms) has a long relaxation time, so it characterizes free water with strong mobility. നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയുടെ സുഷിരങ്ങളിൽ ഈ വെള്ളം നിലനിൽക്കുന്നു, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ സിസ്റ്റത്തിൽ ഒരു ദുർബലമായ കാപ്പിലറി ഫോഴ്സ് മാത്രമേയുള്ളൂ.
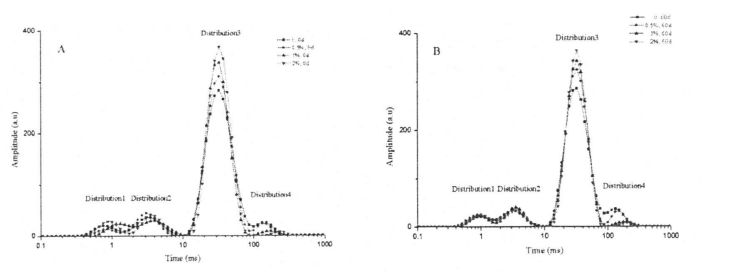
ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ തിരപൂണയ്ക്കുള്ള തിരശ്ചീന വിശ്രമ സമയത്തിന്റെ വിതരണങ്ങളുടെ വളവുകളിൽ FIPMC സമാഹരവും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണവും
കുറിപ്പ്: എ, ബി ട്രാൻസിക്യൂഷൻ സമയത്തെ പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നു (n) എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിന്റെ വിതരണ മാർവുകൾ യഥാക്രമം 0 ദിവസവും 60 ദിവസവും ചേർത്തു
നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ കുഴെച്ചതുമായി താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തുമ്പോൾ യഥാക്രമം 60 ദിവസവും ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സംഭരണവും യഥാക്രമം 60 ദിവസവും ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സംഭരണവും സംഭരിച്ചു. ഉള്ളടക്കം, ഒരു ചെറിയ അളവിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്ത് പ്രധാന ജലപാതക വസ്തുക്കൾ (ചെറിയ അളവിലുള്ള സ്റ്റാർച്ചിനൊപ്പം ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ) മാറ്റാം. മറുവശത്ത്, ടി 21, ടി 24 എന്നിവയുടെ വിതരണ മേഖലകളെ താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തി, വ്യത്യസ്ത ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യൽ സംഭരണ സമയങ്ങളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ അതേ അളവിലുള്ള എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുമായി ചേർത്ത് കാര്യമായ വ്യത്യാസവുമില്ല, ഇത് മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സംഭരണ പ്രക്രിയയിൽ ബന്ധിതമാണ്, പരിസ്ഥിതിയിൽ പ്രതികൂലമായി ബാധിക്കുന്നു. Changes are less sensitive and less affected.
However, there were obvious differences in the height and area of T23 distribution of wet gluten mass that was not frozen and contained different HPMC additions, and with the increase of addition, the height and area of T23 distribution increased (Fig. 3.4). പരിമിതമായ ജലത്തിന്റെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കം എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഗണ്യമായി വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുമെന്ന് ഈ മാറ്റം കാണിക്കുന്നു, ഇത് ഒരു നിശ്ചിത ശ്രേണിയിലെ അധിക തുകയുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്നു. കൂടാതെ, സംഭരണ സമയത്തെ മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ വിപുലീകരണവും, ഒരേ എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഉള്ളടക്കവുമായി നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പിണ്ഡത്തിന്റെ ടി 23 വിതരണത്തിന്റെ ഉയരവും മേഖലയും വ്യത്യസ്ത അളവിൽ കുറയുന്നു. അതിനാൽ, ബന്ധിത വെള്ളവുമായി താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തുമ്പോൾ, ലിമിറ്റഡ് സ്റ്റോറേജിൽ പരിമിതമായ വെള്ളം ഒരു ഉറപ്പ് കാണിച്ചു. Sensitivity. This trend suggests that the interaction between the gluten protein matrix and the confined water becomes weaker. മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിനിടയിൽ കൂടുതൽ ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ തുറന്നുകാട്ടപ്പെടുമാറാകാം, ഇത് താപ ഡിനാറ്ററേഷൻ പീക്ക് ടെമ്പറിന്റെ അളവുകളുമായി പൊരുത്തപ്പെടുന്നതാണ്. പ്രത്യേകിച്ചും, നനഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പിണ്ഡത്തിനുള്ള ടി 23 വിതരണത്തിന്റെ ഉയരവും വിസ്തൃതിയും 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലുമായി കാര്യമായ വ്യത്യാസമില്ല. ജലത്തിന്റെ കുടിയേറ്റവും പുനർവിതരണവും എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് പരിമിതപ്പെടുത്താമെന്നും മരവിപ്പിച്ച സംസ്ഥാനങ്ങളിൽ നിന്ന് സ free ജന്യ സംസ്ഥാനത്തേക്ക് സ stive ജന്യ സംസ്ഥാനത്തേക്ക് പരിവർത്തനം ചെയ്യാമെന്നും ഇത് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
കൂടാതെ, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഉള്ളടക്കമുള്ള ടി 24 പിണ്ഡത്തിന്റെ ടി 24 വിതരണത്തിന്റെ ഉയരവും വിസ്തൃതിയും (ചിത്രം 3.4, a), സ്വതന്ത്ര വെള്ളത്തിന്റെ ഉള്ളടക്കം എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ അളവിൽ നെഗറ്റീവ് ആയി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്നു. This is just the opposite of the Dang distribution. അതിനാൽ, ഈ വ്യതിയാനം സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ശേഷി കൈവശം വയ്ക്കുകയും പരിസരഹിതം വെറും വെള്ളത്തിൽ പരിവർത്തനം ചെയ്യുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നുവെന്ന് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. However, after 60 days of freezing, the height and area of T24 distribution increased to varying degrees, which indicated that the water state changed from restricted water to free-flowing state during the freezing process. This is mainly due to the change of the gluten protein conformation and the destruction of the "layer" unit in the gluten structure, which changes the state of the confined water contained in it. Although the content of freezable water determined by DSC also increases with the extension of freezing storage time, however, due to the difference in the measurement methods and characterization principles of the two, the freezable water and free water are not completely equivalent. For the wet gluten mass added with 2% HPMC, after 60 days of freezing storage, none of the four distributions showed significant differences, indicating that HPMC can effectively retain the water state due to its own water-holding properties and its interaction with gluten. സ്ഥിരതയുള്ള ദ്രവ്യത.
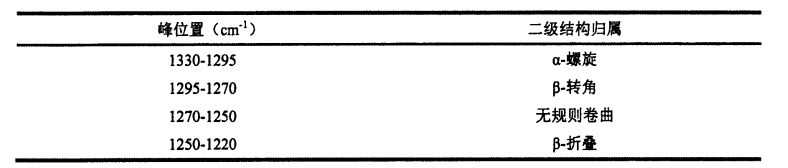
സാധാരണയായി സംസാരിക്കുമ്പോൾ, പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയിൽ നാല് തരങ്ങളായി തിരിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു, α-മടക്കിവെച്ച, β-കോണുകൾ, ക്രമരഹിതമായ അദ്യായം. The most important secondary bonds for the formation and stabilization of the spatial conformation of proteins are hydrogen bonds. Therefore, protein denaturation is a process of hydrogen bond breaking and conformational changes.
ആട്രിബ്യൂഷനും പദവിയും പട്ടിക 3.4 ൽ പട്ടികപ്പെടുത്തിയിട്ടുണ്ട്.
ടാബ് 3.4 ഏറ്റവും ഉയർന്ന സ്ഥാനങ്ങളും ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനകളുടെ അസൈൻമെന്റുകളും എഫ്ടി-ഐആർ സ്പെക്ട്രയിൽ അന്തരീക്ഷം
ചിത്രം 3.5, മിനുസമാർന്ന പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രത്തിന്റെ ഇൻഫ്രാറെഡ് സ്പെക്ട്രമാണ് 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഉള്ളടക്കം. (2001) സമാനമായ കൊടുമുടികളുള്ള ഡീകോൺ വോൾവേറ്റഡ് കൊടുമുടികൾക്ക് അനുയോജ്യമായ രണ്ടാമത്തെ ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് [1321]. ഓരോ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയിലെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്ക മാറ്റങ്ങൾ കണക്കാക്കുന്നതിനായി, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ നാല് സെക്കൻഡറി ഘടനയുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ശതമാനത്തിന്റെ ഉള്ളടക്കം പട്ടിക 3.5 സംഗ്രഹിക്കുന്നു.
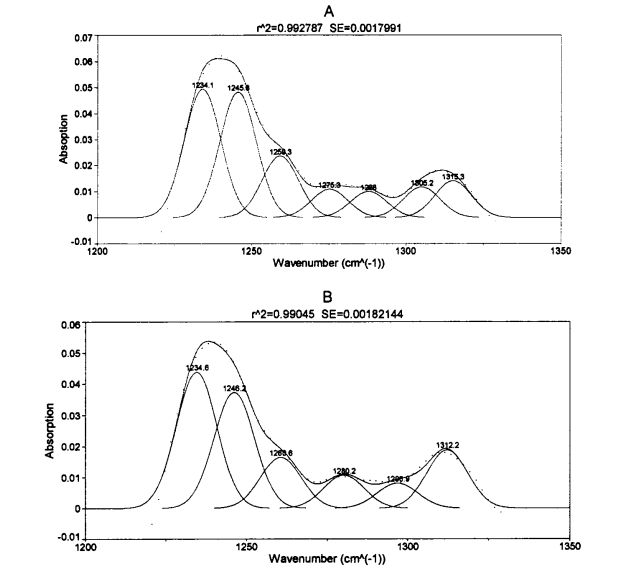
ചിത്രം 3.5 അമിസൈഡ് മൂന്നാമന്റെ അമിസൈഡ് മൂന്നാമൻ III യുടെ അമിസൈഡ് മൂന്നാമൻ സ്ഥാനം, 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസിയിൽ, 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി 0 ഡി (ബി)
With the prolongation of frozen storage time, the secondary structure of gluten protein with different additions of HPMC changed to different degrees. ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയെക്കുറിച്ച് ഫ്രോസൺ സംഭരണവും കൂടാതെ ചേർക്കുകയും ചേർന്ന് അത് കാണാൻ കഴിയും. എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തത് പരിഗണിക്കാതെ, ബി. മടക്കിവെച്ച ഘടന ഏറ്റവും പ്രബലമായ ഘടനയാണ്, ഏകദേശം 60%. After 60 days of frozen storage, add 0%, OB Gluten of 5% and 1% HPMC. The relative content of folds increased significantly by 3.66%, 1.87% and 1.16%, respectively, which was similar to the results determined by Meziani et al. (2011) [l33J]. However, there was no significant difference during frozen storage for gluten supplemented with 2% HPMC. കൂടാതെ, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനയോടെ 0 ദിവസം ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുമ്പോൾ, പേ. മടക്കുകളുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കം ചെറുതായി വർദ്ധിച്ചു, പ്രത്യേകിച്ചും സങ്കലന തുക 2% ആയിരിക്കുമ്പോൾ, പേ. മടക്കുകളുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കം 2.01% വർദ്ധിച്ചു. D. മടക്കിവെച്ച ഘടന ഇന്റർമോളിക്യുലർ പിയിലേക്ക് തിരിക്കാം p. മടക്കിക്കളയുന്നത് (പ്രോട്ടീൻ തന്മാത്രകളുടെ സംയോജനം മൂലമാണ് സംഭവിക്കുന്നത്), ആന്റിപാരല്ലൽ പി. മടക്കിക്കളയുക, സമാന്തര പി. മൂന്ന് ഉപജനകം മടക്കിക്കളയുന്നു, മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയിൽ സബ്സ്ട്രക്ചർ ഏത് സബ്സ്ട്രക്ടറാണ് സംഭവിക്കുന്നത് എന്ന് നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നത് ബുദ്ധിമുട്ടാണ്
മാറ്റി. എസ്-ടൈപ്പ് ഘടനയുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവ് സ്ഥിരമായ അനുരൂപീകരണത്തിന്റെ കാഠിന്യത്തിന്റെയും ജലചനത്തിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവിന് കാരണമാകുമെന്ന് ചില ഗവേഷകർ വിശ്വസിക്കുന്നു [41], മറ്റ് ഗവേഷകർ എന്നിവരാണ് പി. മടക്ക ഘടനയിലെ വർദ്ധനവ് പുതിയ β മടങ്ങ് രൂപപ്പെടുന്നതിനാൽ ഹൈഡ്രജൻ ബോണ്ടിംഗ് പരിപാലിക്കുന്ന ഘടനാപരമായ ശക്തി ദുർബലമാകുന്നതിനൊപ്പം [421]. The- ലെഫ്റ്റ് ഘടനയിലെ വർദ്ധനവ് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നത്, ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ബോണ്ടുകളിലൂടെ പ്രോട്ടീൻ പോളിമറൈസ് ചെയ്യുന്നു, ഇത് കുറഞ്ഞ ഫീൽഡ് ന്യൂക്ലിയർ മേഗ്നിറ്റിക് അനുരണനം അളക്കുന്ന തിരശ്ചീന ഡെനാറ്ററേഷന്റെ വിതരണത്തിന്റെ വിതരണവും. Protein denaturation. On the other hand, added 0.5%, 1% and 2% HPMC gluten protein α-whirling. ഫ്രീസിംഗ് സമയത്തിന്റെ നീണ്ടുനിൽക്കുന്ന ഹെലിക്സിന്റെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കം യഥാക്രമം 0.95%, 4.42%, 2.03 ശതമാനം വർദ്ധിച്ചു, ഇത് വാങിനൊപ്പം സ്ഥിരത പുലർത്തുന്നു. (2014) സമാനമായ ഫലങ്ങൾ കണ്ടെത്തി [134]. 0 of gluten without added HPMC. ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ പ്രക്രിയയിൽ ഹെലിക്സിന്റെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിൽ കാര്യമായ മാറ്റമൊന്നുമില്ല, പക്ഷേ 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രീസ് വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ. There were significant differences in the relative content of α-whirling structures.
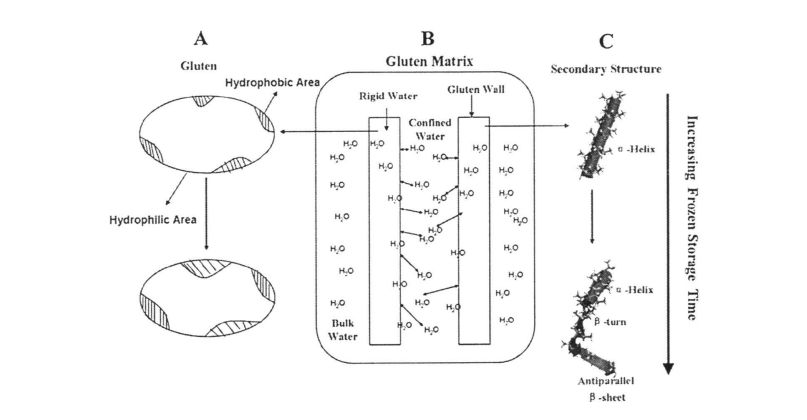
ചിത്രം 3.6 ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് മൊീലി എക്സ്പോഷറിന്റെ (എ), ജല പുനർവിതരണം (ബി), ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ മാട്രിക്സിലെ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടന മാറ്റങ്ങൾ (സി) എന്നിവയുടെ സ്കീമാറ്റിക് വിവരണം 【31'138
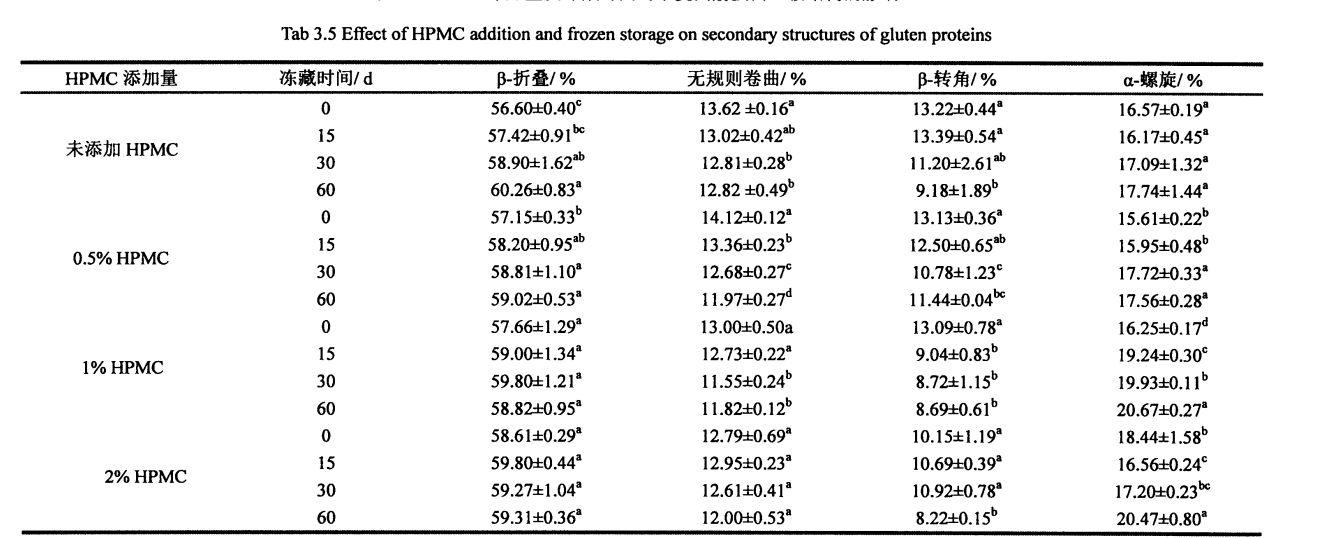
ഫ്രീസിംഗ് സമയം വിപുലീകരണമുള്ള എല്ലാ സാമ്പിളുകളും, പി. കോണുകളുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കങ്ങൾ ഗണ്യമായി കുറഞ്ഞു. ഫ്രീസിംഗ് ചികിത്സയോട് β തിരിയുന്നത് [135]-തിരിവ് വളരെ സെൻസിറ്റീവ് ആണെന്ന് ഇത് കാണിക്കുന്നു [. 1361], എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തതാണോ വേണ്ടയോ എന്ന്. Wellner, et a1. . ക്ലൂട്ടൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ക്രമരഹിതമായ കോയിയറിന്റെ ഘടനയുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക ഉള്ളടക്കം ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിൽ കാര്യമായ മാറ്റമൊന്നുമില്ലെങ്കിൽ, മറ്റ് സാമ്പിളുകൾ ഗണ്യമായി കുറഞ്ഞു, ഇത് ഐസ് പരലുകൾ തീർപ്പാക്കിയേക്കാം. കൂടാതെ, 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രീസുചെയ്തപ്പോൾ, α-ഹെലിക്സ്, β-ഷീറ്റ്, β-ടേൺ ഘടന, 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി എന്നിവ ചേർത്ത് ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ഘടന, എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഇല്ലാതെ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീൻ എന്നതിൽ നിന്ന് ഗണ്യമായി കഴിഞ്ഞു. This may indicate that there is an interaction between HPMC and gluten protein, forming new hydrogen bonds and then affecting the conformation of the protein; or HPMC absorbs the water in the pore cavity of the protein space structure, which deforms the protein and leads to more changes between the subunits. close. The increase of the relative content of β-sheet structure and the decrease of the relative content of β-turn and α-helix structure are consistent with the above speculation. During the freezing process, the diffusion and migration of water and the formation of ice crystals destroy the hydrogen bonds that maintain the conformational stability and expose the hydrophobic groups of proteins. In addition, from the perspective of energy, the smaller the energy of the protein, the more stable it is. At low temperature, the self-organization behavior (folding and unfolding) of protein molecules proceeds spontaneously and leads to conformational changes.
ഉപസംഹാരമായി, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിക് ഗുണങ്ങളും പ്രോട്ടീനുമായുള്ള ആശയവിനിമയവും, ഫ്രീറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ദ്വിതീയ ഘടനയുടെ മാറ്റത്തെ തടസ്സപ്പെടുത്തുന്നതിനും പ്രോട്ടീൻ കോൺഫോർംഫോർമർ സ്ഥിരമായി നിലനിർത്തുന്നതിനും എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ ഉയർന്ന അളവ്.
3.3.6 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ഉപരിതലത്തിൽ സംഭരണ സമയം മരവിപ്പിക്കൽ സമയം
ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിക്, ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു. Generally, the protein surface is composed of hydrophilic groups, which can bind water through hydrogen bonding to form a hydration layer to prevent protein molecules from agglomerating and maintain their conformational stability. The interior of the protein contains more hydrophobic groups to form and maintain the secondary and tertiary structure of the protein through the hydrophobic force. പ്രോട്ടീനുകളുടെ ഡിനാന്റേഷൻ പലപ്പോഴും ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ എക്സ്പോഷർ ചെയ്യുന്നതിലൂടെയും ഉപരിതല ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിസിറ്റി വർദ്ധിച്ചതുമാണ്.
Tab3.6 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ സ്വാധീനം, ഉപരിതലത്തിൽ ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിസിറ്റി

കുറിപ്പ്: അതേ നിരയിൽ, m, b എന്നിവയില്ലാത്ത ഒരു സൂപ്പർസ്ക്രിപ്റ്റ് കത്ത് ഉണ്ട്, ഇത് ഒരു പ്രധാന വ്യത്യാസമുണ്ടെന്ന് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു (<0.05);
ഒരേ നിരയിലെ വ്യത്യസ്ത സൂപ്പർസ്ക്രിപ്റ്റ് വലിയ അക്ഷരങ്ങൾ കാര്യമായ വ്യത്യാസം (<0.05) സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു;
ശീതീകരിച്ച 60 ദിവസത്തിനുശേഷം, 0%, ഒ. 3%, 1%, 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി എന്നിവ യഥാക്രമം 70.53%, 55.63 ശതമാനം ഉയർന്ന് 35.63 ശതമാനം ഉയർന്ന് 35.63 ശതമാനം ഉയർന്ന് 35.63 ശതമാനം ഉയർന്നു. In particular, the surface hydrophobicity of the gluten protein without adding HPMC after being frozen for 30 days has increased significantly (P<0.05), and it is already greater than the surface of the gluten protein with 1% and 2% HPMC added after freezing for 60 days Hydrophobicity. At the same time, after 60 days of frozen storage, the surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein added with different contents showed significant differences. However, after 60 days of frozen storage, the surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein added with 2% HPMC only increased from 19.749 to 26.995, which was not significantly different from the surface hydrophobicity value after 30 days of frozen storage, and was always lower than other the value of the surface hydrophobicity of the sample. This indicates that HPMC can inhibit the denaturation of gluten protein, which is consistent with the results of DSC determination of the peak temperature of heat deformation. പ്രോട്ടീൻ ഘടനയെ പുനരുജ്ജീവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയെ തടയാൻ കഴിയുന്നതിനാലാണിത്, അതിന്റെ ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിറ്റി കാരണം,
ദ്വിതീയ ബോണ്ടുകളിലൂടെ പ്രോട്ടീൻ ഉപരിതലത്തിൽ ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകളുമായി സംയോജിപ്പിക്കാൻ എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ദ്വിതീയ ബോണ്ടുകളിലൂടെ സംയോജിപ്പിക്കാൻ കഴിയും, അതുവഴി പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ ഉപരിതല സവിശേഷതകൾ മാറ്റുകയും ഹൈഡ്രോഫോബിക് ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ എക്സ്പോഷർ ചെയ്യുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു (പട്ടിക 3.6).
3.3.7 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ, ഗ്ലൂറ്റന്റെ മൈക്രോ-നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയിൽ സംഭരണ സമയം മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നു
The continuous gluten network structure contains many pores to maintain the carbon dioxide gas produced by the yeast during the proofing process of the dough. Therefore, the strength and stability of the gluten network structure are very important to the quality of the final product, such as specific volume, quality, etc. Structure and sensory assessment. മൈക്രോസ്കോപ്പിക് പോയിന്റിൽ നിന്ന്, വസ്തുക്കളുടെ മൈക്രോസ്കോപ്പി സ്കാനിംഗ് ചെയ്തതിലൂടെ മെറ്റീരിയലിന്റെ രൂപാന്തരചനങ്ങൾ നിരീക്ഷിക്കാൻ കഴിയും, ഇത് മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയിൽ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയുടെ മാറ്റത്തിന് പ്രായോഗിക അടിസ്ഥാനം നൽകുന്നു.
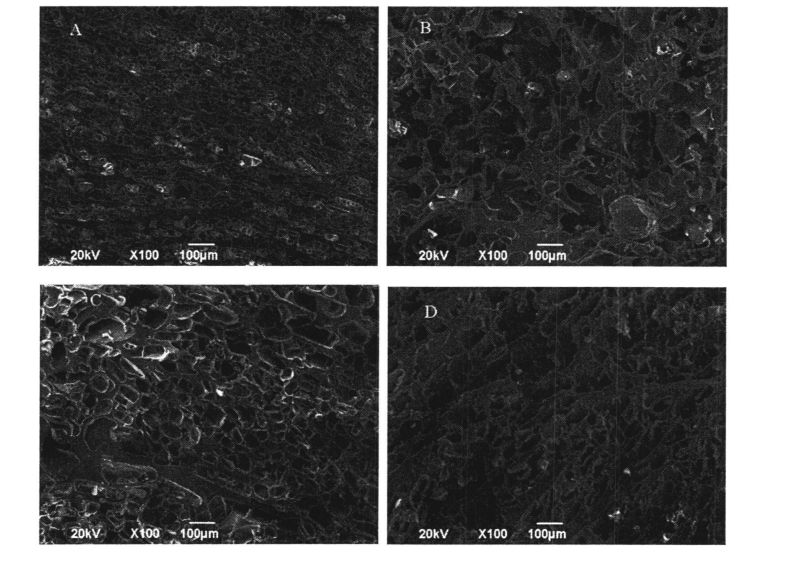
കുറിപ്പ്: 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് എച്ച്പിഎംസിയും ഫ്രീസുചെയ്തുക്കാതെ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ നെറ്റ്വർക്കിന്റെ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചർ; 60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് എച്ച്പിഎംസിയും ഫ്രീസുചെയ്തുക്കാതെ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ നെറ്റ്വർക്കിന്റെ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചറിന്റെ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചർ ആണ്; സി ആണ് 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്ത് 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ചേർത്ത് ഫ്രീസുചെയ്തതും 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രീസുചെയ്തതുമായ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ നെറ്റ്വർട്ടിന്റെ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചറിന്റെ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചർ: ഡി 6% hpmc
ചെറിയ ഏകദേശ പോറസ് സ്പോഞ്ച് പോലുള്ള മോർഫോളജി. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, 60 ദിവസത്തെ ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന് ശേഷം, എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഇല്ലാതെ ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചറിലെ സെല്ലുകൾ, അതായത്, അദൃശ്യമായ വിതരണം (ചിത്രം 3.7, എ, ബി) the disulfide bond, which affects the strength and integrity of the structure. KontoNGiiorgos & Goft (2006), kontuuten നെറ്റ്വർക്കിന്റെ ഇന്റർസ്റ്റോഡിയോഗോസ് (2007), FELLESE-ഷ്രീം കാരണം ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ നെറ്റ്വർക്കിയർഗോസ് (2007), ഘടനാപരമായ തടസ്സം [138] 1391]. കൂടാതെ, നിർജ്ജലീകരണം കാരണം, സ്പോഞ്ചി ഘടനയിൽ താരതമ്യേന ഇടതൂർന്ന നാരുകളുള്ള ഘടന സൃഷ്ടിക്കപ്പെട്ടു, ഇത് 15 ദിവസത്തിനുശേഷം ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന് ശേഷമുള്ള കാരണമായിരിക്കാം, കാരണം ഇത് കൂടുതൽ തിമിരരൂപകൽപ്പനകളും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണവും സൃഷ്ടിച്ചു. ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ ഘടന ഹ്രസ്വ സമയത്തേക്ക് സാരമായി കേടായിരുന്നില്ല, അത് വാങിനൊപ്പം സ്ഥിരത പുലർത്തുന്നു. (2014) സമാനമായ പ്രതിഭാസങ്ങൾ നിരീക്ഷിച്ചു [134]. അതേസമയം, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ മൈക്രോടെക്ചറിന്റെ നാശം ഫ്രീയർ വാട്ടർ മൈഗ്രേഷൻ, പുനർവിതരണം എന്നിവയിലേക്ക് നയിക്കുന്നു, ഇത് കുറഞ്ഞ ഫീൽഡ് ടൈം-ഡൊമെയ്ൻ മെഗാനിറ്റിക് അനുരണനങ്ങൾ (ടിഡി-എൻഎംആർ) അളവുകൾ (ടിഡി-എൻഎംആർ) അളവുകൾ (ടിഡി-എൻഎംആർ) അളവുകൾ (ടിഡി-എൻഎംആർ) അളക്കുന്നു. Some studies [140, 105] reported that after several freeze-thaw cycles, the gelatinization of rice starch and the structural strength of the dough became weaker, and the water mobility became higher. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, 60 ദിവസത്തെ ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന് ശേഷം, 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിനൊപ്പം ഗ്ലൂസെൻറെ മൈക്രോസ്ട്രക്ചർ കുറവ് മാറി, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലില്ലാതെ ചെറിയ കോശങ്ങളും കൂടുതൽ പതിവ് ആകൃതികളും (ചിത്രം 3.7, ബി, ഡി). ശരിയാക്കി ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ ഘടനയുടെ നാശത്തെ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയെ ഫലപ്രദമായി തടയാൻ എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ഫലപ്രദമായി തടയാൻ കഴിയുമെന്ന് ഇത് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
3.4 അധ്യായം സംഗ്രഹം
This experiment investigated the rheology of wet gluten dough and gluten protein by adding HPMC with different contents (0%, 0.5%, 1% and 2%) during freezing storage (0, 15, 30 and 60 days). properties, thermodynamic properties, and effects of physicochemical properties. The study found that the change and redistribution of water state during the freezing storage process significantly increased the freezable water content in the wet gluten system, which led to the destruction of the gluten structure due to the formation and growth of ice crystals, and ultimately caused the processing properties of the dough to be different. Deterioration of product quality. The results of frequency scanning showed that the elastic modulus and viscous modulus of the wet gluten mass without adding HPMC decreased significantly during the freezing storage process, and the scanning electron microscope showed that its microstructure was damaged. The content of free sulfhydryl group was significantly increased, and its hydrophobic group was more exposed, which made the thermal denaturation temperature and surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein significantly increased. However, the experimental results show that the addition of I-IPMC can effectively inhibit the changes in the structure and properties of wet gluten mass and gluten protein during freezing storage, and within a certain range, this inhibitory effect is positively correlated with the addition of HPMC. This is because HPMC can reduce the mobility of water and limit the increase of the freezable water content, thereby inhibiting the recrystallization phenomenon and keeping the gluten network structure and the spatial conformation of the protein relatively stable. ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ച ഘടനയുടെ സമഗ്രതയെ ഫലപ്രദമായി നിലനിർത്താൻ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ മാത്രമേ ഇത് കാണിക്കുന്നത്, അതുവഴി ഉൽപ്പന്ന നിലവാരം ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നു.
ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സംഭരണത്തിന്റെ ഘടനയിലും സവിശേഷതകളിലും എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ
4.1 ആമുഖം
മോണോമറിനെന്ന നിലയിൽ ഗ്ലൂക്കോസ് ഉള്ള ഒരു ശൃംഖല പോളിസാക്കുകളാണ് അന്നജം. കീ) രണ്ട് തരം. From a microscopic point of view, starch is usually granular, and the particle size of wheat starch is mainly distributed in two ranges of 2-10 pro (B starch) and 25-35 pm (A starch). From the perspective of crystal structure, starch granules include crystalline regions and amorphous regions (je, non-crystalline regions), and the crystal forms are further divided into A, B, and C types (it becomes V-type after complete gelatinization). സാധാരണയായി, ക്രിസ്റ്റലിൻ പ്രദേശം അടങ്ങിയത് അമിലോപെക്റ്റിൻ, പ്രദേശം പ്രധാനമായും അമിലോസ് അടങ്ങിയിരിക്കുന്നു. This is because, in addition to the C chain (main chain), amylopectin also has side chains composed of B (Branch Chain) and C (Carbon Chain) chains, which makes amylopectin appear "tree-like" in raw starch. ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ രൂപീകരിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഒരു പ്രത്യേക മാർഗത്തിലാണ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റ് ബണ്ടിലിന്റെ ആകൃതി ക്രമീകരിക്കുന്നത്.
Starch is one of the main components of flour, and its content is as high as about 75% (dry basis). At the same time, as a carbohydrate widely present in grains, starch is also the main energy source material in food. കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, അന്നജം കൂടുതലും വിതരണം ചെയ്യുന്നു, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീന്റെ നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയുമായി അറ്റാച്ചുചെയ്തു. During processing and storage, starches often undergo gelatinization and aging stages.
Among them, starch gelatinization refers to the process in which starch granules are gradually disintegrated and hydrated in a system with high water content and under heating conditions. It can be roughly divided into three main processes. 1) വിപരീത ജല ആഗിരണം ഘട്ടം; before reaching the initial temperature of gelatinization, the starch granules in the starch suspension (Slurry) keep their unique structure unchanged, and the external shape and internal structure basically do not change. വളരെ കുറച്ച് ലയിക്കുന്ന അന്നജം മാത്രം വെള്ളത്തിൽ ചിതറിക്കിടക്കുന്നു, മാത്രമല്ല അതിന്റെ യഥാർത്ഥ അവസ്ഥയിലേക്ക് പുന ored സ്ഥാപിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യും. 2) The irreversible water absorption stage; താപനില വർദ്ധിക്കുമ്പോൾ, അന്നജം സ്ഫടിലൈറ്റ് ബണ്ടിലുകൾ തമ്മിലുള്ള വിടവ്, മാറ്റാനാവാത്ത രീതിയിൽ വലിയ അളവിൽ വെള്ളം ഉയർത്തുന്നു, അന്നജം വീർക്കുന്നു, അന്നജം തന്മാത്രകൾ തമ്മിലുള്ള ഹൈഡ്രജൻ ബോണ്ടുകൾ തകർന്നു. അത് നീട്ടി, പരലുകൾ അപ്രത്യക്ഷമാകും. At the same time, the birefringence phenomenon of starch, that is, the Maltese Cross observed under a polarizing microscope, begins to disappear, and the temperature at this time is called the initial gelatinization temperature of starch. 3) Starch granule disintegration stage; starch molecules completely enter the solution system to form starch paste (Paste/Starch Gel), at this time the viscosity of the system is the largest, and the birefringence phenomenon completely disappears, and the temperature at this time is called the complete starch gelatinization temperature, the gelatinized starch is also called α-starch [141]. When the dough is cooked, the gelatinization of starch endows the food with its unique texture, flavor, taste, color, and processing characteristics.
Many studies have shown that the gel strength of starch paste decreases, it is easy to age, and its quality deteriorates under the condition of freezing storage, such as Canet, et a1. (2005) studied the effect of freezing temperature on the quality of potato starch puree; Ferrero, et a1. (1993) investigated the effects of freezing rate and different types of additives on the properties of wheat and corn starch pastes [151-156]. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, അന്നജം ഗ്രാനുലുകളുടെ (നേറ്റീവ് അന്നജം) ഘടനയെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന്റെ ഫലത്തിൽ താരതമ്യേന കുറച്ച് റിപ്പോർട്ടുകൾ ഉണ്ട്, അത് കൂടുതൽ പര്യവേക്ഷണം ചെയ്യേണ്ടതുണ്ട്. ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ (പ്രീ-വേവിച്ച ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഒഴികെ) ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന് കീഴിലുള്ള കുറ്റമില്ലാത്ത ഗ്രാനുലുകളുടെ രൂപത്തിലാണ്. Therefore, studying the structure and structural changes of native starch by adding HPMC has a certain effect on improving the processing properties of frozen dough. പ്രാധാന്യം.
4.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കളും രീതികളും
4.2.1 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കൾ
ഗോതമ്പ് അന്നജം ബിൻഷ ou സോങ്യു ഫുഡ് കോ., ലിമിറ്റഡ്.; എച്ച്പിഎംസി അലദ്ദിൻ (ഷാങ്ഹായ്) കെമിക്കൽ റിജന്റ് കോ.
4.2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഉപകരണം
ഉപകരണങ്ങളുടെ പേര്
HH ഡിജിറ്റൽ നിരന്തരമായ താപനില വാട്ടർ ബാത്ത്
Sx2.4.10 മഫിൽ ചൂള
Dhg. 9070A Blast Drying Oven
കെഡിസി. 160 മണിക്കൂർ അതിവേഗ ശീതീകരിച്ച സെൻട്രിഫ്യൂജ്
ഡിസ്കവറി ആർ 3 റൊട്ടഫർ റിമീറ്റർ
ചോദ്യം. 200 ഡിഫറൻഷ്യൽ സ്കാൻ ചെയ്യുന്നു കലോറിമീറ്റർ
Sx2.4.10 മഫിൽ ചൂള
നിര്മ്മാതാവ്
ജിയാങ്സു ജിൻചെംഗ് ഗ്വോഷ്ംഗ് പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഉപകരണ ഫാക്ടറി
സാർട്ടോറിയസ്, ജർമ്മനി
ഹേർ ഗ്രൂപ്പ്
ഹുവാങ്ഷി ഹെങ്ഫെങ് മെഡിക്കൽ ഉപകരണ കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
അമേരിക്കൻ ടിഎ കമ്പനി
അമേരിക്കൻ ടിഎ കമ്പനി
റിഗകു മാനുഫാക്ചർ കോ., ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ഹുവാങ്ഷി ഹെങ്ഫെങ് മെഡിക്കൽ ഉപകരണ കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
4.2.3 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക രീതി
4.2.3.1 അന്നജം സസ്പെൻഷന്റെ ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സംഭരണവും
4.2.3.2 റിയോളജിക്കൽ ഗുണങ്ങൾ
അനുബന്ധ മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സമയത്തോടുകൂടിയ മേൽപ്പറഞ്ഞ സാമ്പിളുകൾ പുറത്തെടുക്കുക, 4 മണിക്കൂർ ഇക്വിലിബ്രേറ്റ് ചെയ്യുക, തുടർന്ന് റൂം താപനില പൂർണ്ണമായും ഉരുകിപ്പോകുന്നതുവരെ നീങ്ങുക.
(1) അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈനേഷൻ സവിശേഷതകൾ
ഈ പരീക്ഷണത്തിൽ, അന്നജത്തിന്റെ ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈസേഷൻ സവിശേഷതകൾ അളക്കുന്നതിന് ഒരു വേഗത്തിലുള്ള വിസ്കോറിന് പകരം ഒരു വാചാടി ഉപയോഗിച്ചു. BAAE ET at a1 കാണുക. (2014) രീതി [1571] നേരിയ പരിഷ്ക്കരണത്തോടെ. നിർദ്ദിഷ്ട പ്രോഗ്രാം പാരാമീറ്ററുകൾ ഇപ്രകാരമാണ്: 40 മില്ലിന്റെ വ്യാസമുള്ള ഒരു പ്ലേറ്റ് ഉപയോഗിക്കുക, വിടവ് (ജിഎപി) 1000 മില്ലീമീറ്റർ, റൊട്ടേഷൻ വേഗത 5 rad / s ആണ്; I) 1 മിനിറ്റിനായി 50 ° C ന് ഇൻകുബേറ്റ്; ii) at 5. C/min heated to 95°C; iii) 2.5 മിനുട്ട് 2.5 മിനിറ്റ്, iv) എന്നിട്ട് 5 ° C / MIN- ൽ 50 ° C വരെ തണുപ്പിക്കുക; v) lastly held at 50°C for 5 min.
1.5 മില്ലി സാമ്പിൾ പരിഹാരം വരച്ച് റിക്കോർമീറ്റർ സാമ്പിൾ ഘട്ടത്തിന്റെ മധ്യഭാഗത്ത് ചേർക്കുക, മുകളിലുള്ള പ്രോഗ്രാം പാരാമീറ്ററുകൾ അനുസരിച്ച് സാമ്പിളിന്റെ ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈസേഷൻ സ്വത്തുക്കൾ, അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈനേഷൻ കർവ് എന്ന നിലയിൽ (° C). According to GB/T 14490.2008 [158], the corresponding gelatinization characteristic indicators—gelatinization peak viscosity (field), peak temperature (Ang), minimum viscosity (high), final viscosity (ratio) and decay value (Breakdown) are obtained. Value, BV) and regeneration value (Setback Value, SV), wherein, decay value = peak viscosity - minimum viscosity; setback value = final viscosity - minimum viscosity. Each sample was repeated three times.
4.2.3.3 സ്റ്റാർച്ച് പേസ്റ്റ് ജെൽ പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികൾ
(1) സാമ്പിൾ തയ്യാറെടുപ്പ്
Take 2.5 g of amyloid and mix it with distilled water in a ratio of 1:2 to make starch milk. Freeze at 18°C for 15 d, 30 d, and 60 d. ഒരേ നിലവാരം മാറ്റിസ്ഥാപിക്കുന്നതിന് 0.5, 1, 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി (W / W) ചേർക്കുക, മറ്റ് തയ്യാറെടുപ്പ് രീതികൾ മാറ്റമില്ലാതെ തുടരുന്നു. മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന ചികിത്സ പൂർത്തിയാക്കിയ ശേഷം, അത് പുറത്തെടുക്കുക, 4 മണിക്കൂർ 4 f ° C ൽ സമവാക്രം, തുടർന്ന് അത് പരീക്ഷിക്കുന്നതുവരെ ചൂണ്ടിക്കാണിക്കുന്നു.
(3) അന്നജം ജെൽഫ്റ്റർ (ജെൽ ശക്തി)
4.2.3.4 തെർമോഡൈനാമിക് പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികൾ
(1) സാമ്പിൾ തയ്യാറെടുപ്പ്
അനുബന്ധ ചികിത്സാ സമയത്തിന് ശേഷം, സാമ്പിളുകൾ പുറത്തെടുത്ത് പൂർണ്ണമായും ഉരുകി, 48 മണിക്കൂർ അടുപ്പത്തുവെച്ചു ഉണങ്ങി. അവസാനമായി, ഒരു സോളിഡ് പൊടി സാമ്പിൾ ലഭിക്കാൻ 100 മെഷ് അരിപ്പയിലൂടെ നിലത്തുവീഴുന്നു (എക്സ്ആർഡി പരിശോധനയ്ക്ക് അനുയോജ്യം). Xie, et a1 കാണുക. (2014) method for sample preparation and determination of thermodynamic properties '1611, weigh 10 mg of starch sample into a liquid aluminum crucible with an ultra-micro analytical balance, add 20 mg of distilled water in a ratio of 1:2, press and seal it and place it at 4 °C In the refrigerator, equilibrated for 24 h. ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുക 18 ° C (0, 15, 30, 60 ദിവസം). അന്നജത്തിന്റെ അനുബന്ധ നിലവാരം മാറ്റിസ്ഥാപിക്കാൻ 0.5%, 1%, 2% (W / W) HPMC ചേർക്കുക, മറ്റ് ഒരുക്കങ്ങൾ രീതികൾ മാറ്റമില്ലാതെ തുടരുന്നു. മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സംഭരണ സമയത്തിന് ശേഷം, 4 മണിക്കൂർ 4 ° C ന് ക്രൂസിബിൾ, സമവാക്രം പുറത്തെടുക്കുക.
(3) ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈസേഷൻ താപനിലയും എന്തൽപി മാറ്റവും നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നു
ശൂന്യമായത് ഒരു റഫറൻസായി നിർവഹിക്കാനാവാത്തത്, നൈട്രജൻ ഫ്ലോ റേറ്റ് 50 മില്ലിഗ്രാം 50 മില്ലിമീറ്ററായിരുന്നു, 5 മിനിറ്റ് / മില്ലിന് 20 ° C വരെ തുല്യമായി. Finally, the heat flow (Heat Flow, mW) is the DSC curve of the ordinate, and the gelatinization peak was integrated and analyzed by Universal Analysis 2000. Each sample was repeated at least three times.
4.2.3.5 XRD അളവ്
ഇന്നൊദ് ഫ്രോസൺ അന്നജം സാമ്പിളുകൾ 48 ൻ ° C ൽ അടുപ്പത്തുവെച്ചു വറ്റിച്ചു, തുടർന്ന് നിലത്തു നിലത്തു വച്ചിരുന്നു, തുടർന്ന് അരങ്ങും 100 മെഷ് സിഷ് സിഷ് സീ സെന്നുകുത്തി. മേൽപ്പറഞ്ഞ സാമ്പിളുകളുടെ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത തുക എടുക്കുക, ഡി / മാക്സ് 2500 വി തരം ഉപയോഗിക്കുക x ഉപയോഗിക്കുക. ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ ഫോമും ആപേക്ഷിക ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റിയും എക്സ്-റേ ഡിഫ്രാക്റ്റോമീറ്റർ നിർണ്ണയിച്ചു. The experimental parameters are voltage 40 KV, current 40 mA, using Cu. Ks as X. ray source. At room temperature, the scanning angle range is 30--400, and the scanning rate is 20/min. Relative crystallinity (%) = crystallization peak area/total area x 100%, where the total area is the sum of the background area and the peak integral area [1 62].
Take 0.1 g of the dried, ground and sieved amyloid into a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 10 mL of distilled water to it, shake it well, let it stand for 0.5 h, and then place it in a 95°C water bath at a constant temperature. 30 മിനിറ്റ് കഴിഞ്ഞ്, ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ പൂർത്തിയായ ശേഷം, കേന്ദ്രീകൃത ട്യൂബ് പുറത്തെടുത്ത് ദ്രുത തണുപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന് 10 മിനിറ്റ് ഇടുക. അവസാനമായി, 20 മിനിറ്റിന് 5000 ആർപിഎമ്മിൽ കേന്ദ്രീകൃതമായി, ഒരു അന്തരീക്ഷം നേടുന്നതിന് അപ്രതീക്ഷിത ഭക്ഷണം ഒഴിക്കുക. വീക്കം പവർ = മഴപ്പാടി പിണ്ഡം / സാമ്പിൾ പിണ്ഡം [163].
4.2.3.7 ഡാറ്റ വിശകലനവും പ്രോസസ്സിംഗും
വ്യക്തമാക്കിയെങ്കിൽ എല്ലാ പരീക്ഷണങ്ങളും കുറഞ്ഞത് മൂന്ന് തവണയെങ്കിലും ആവർത്തിച്ചു, പരീക്ഷണാത്മക ഫലങ്ങൾ ശരാശരി, സ്റ്റാൻഡേർഡ് വ്യതിയാനമായി പ്രകടിപ്പിച്ചു. എസ്പിഎസ്എസ് സ്റ്റാറ്റിസ്റ്റിക് 19 0.05 എന്ന പ്രാധാന്യ നിലവാരത്തിലുമായി വേരിയൻസ് (വേരിയൻസ്, അനോവ) വിശകലനം ഉപയോഗിച്ചു; correlation charts were drawn using Origin 8.0.
According to GB 50093.2010, GB/T 5009.9.2008, GB 50094.2010 (78-s0), the basic components of wheat starch - moisture, amylose/amylopectin and ash content were determined. ഫലങ്ങൾ പട്ടിക 4 ൽ കാണിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു. 1 കാണിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു.
ഗോതമ്പ് അന്നഖത്തിന്റെ ഘടകത്തിന്റെ 4.1 ഉള്ളടക്കം ടാപ്പുചെയ്യുക
The starch suspension with a certain concentration is heated at a certain heating rate to make the starch gelatinized. ജെലാറ്റിനിഫൈയിലേക്ക് ആരംഭിച്ചതിന് ശേഷം, പ്രക്ഷുബ്ധമായ ദ്രാവകം അന്നജത്തിന്റെ വ്യാപനം കാരണം ക്രമേണ ഒട്ടിക്കും, വിസ്കോസിറ്റി തുടർച്ചയായി വർദ്ധിക്കുന്നു. തുടർന്ന്, അന്നജം വിള്ളൽ, വിസ്കോസിറ്റി കുറയുന്നു. ഒട്ടിക്കുന്ന ഒരു തണുപ്പിക്കൽ നിരക്കിലാണ് ഒട്ടിക്കുമ്പോൾ, പേസ്റ്റ് ജെൽ ചെയ്യും, വിസ്കോസിറ്റി മൂല്യം വർദ്ധിക്കും. 50 ഡിഗ്രി സെൽഷ്യസ് വരെ തണുപ്പിക്കുമ്പോൾ വിസ്കോസിറ്റി മൂല്യം അന്തിമ വിസ്കോസിറ്റി മൂല്യമാണ് (ചിത്രം 4.1).
Table 4.2 lists the influence of several important indicators of starch gelatinization characteristics, including gelatinization peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value and appreciation value, and reflects the effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on starch paste. രാസ ഗുണങ്ങളുടെ ഫലങ്ങൾ. The experimental results show that the peak viscosity, the minimum viscosity and the final viscosity of starch without frozen storage increased significantly with the increase of HPMC addition, while the decay value and recovery value decreased significantly. Specifically, the peak viscosity gradually increased from 727.66+90.70 CP (without adding HPMC) to 758.51+48.12 CP (adding 0.5% HPMC), 809.754-56.59 CP (adding 1 %HPMC), and 946.64+9.63 CP (adding 2% HPMC); the minimum viscosity was increased from 391.02+18.97 CP (blank not adding) to 454.95+36.90 (adding O .5% HPMC), 485.56+54.0.5 (add 1% HPMC) and 553.03+55.57 CP (add 2% HPMC); the final viscosity is from 794.62.412.84 CP ( Without adding HPMC) increased to 882.24±22.40 CP (adding 0.5% HPMC), 846.04+12.66 CP (adding 1% HPMC) and 910.884-34.57 CP (adding 2 %HPMC); however, the attenuation value gradually decreased from 336.644-71.73 CP (without adding HPMC) to 303.564-11.22 CP (adding 0.5% HPMC), 324.19±2.54 CP (Add
1% എച്ച്പിഎംസിസി), 393.614-45.94 സിപി (2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി), 153.60 + 6.13 വരെ (എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഇല്ലാതെ) 427.29 + 14.50 സിപി (36.484-41.39 സിപി), 360.484-41.39 സിപി (എച്ച്പിഎംസി), 357.85 + 21.00 സി പി (2% എച്ച്പിഎംസിഐ ചേർത്തു). അച്ചിയോകൻ, സുവാന്താരകൻ, സുമന്താരികക (2008), ഹുവാങ് (2008), ഹുവാങ് (2008), ഹുവാങ് (2008), ഹുവാങ് (2008), ഹുവാങ് (2008), ഹുവാങ് (2008), ഹുവാങ് എന്നിങ്ങനെയുള്ള ജലോക്കോലോയിഡുകളും ഇതാണ്. This may be mainly because HPMC acts as a kind of hydrophilic colloid, and the addition of HPMC increases the gelatinization peak viscosity due to the hydrophilic group on its side chain which makes it more hydrophilic than starch granules at room temperature. In addition, the temperature range of the thermal gelatinization process (thermogelation process) of HPMC is larger than that of starch (results not shown), so that the addition of HPMC can effectively suppress the drastic decrease in viscosity due to the disintegration of starch granules. Therefore, the minimum viscosity and final viscosity of starch gelatinization increased gradually with the increase of HPMC content.
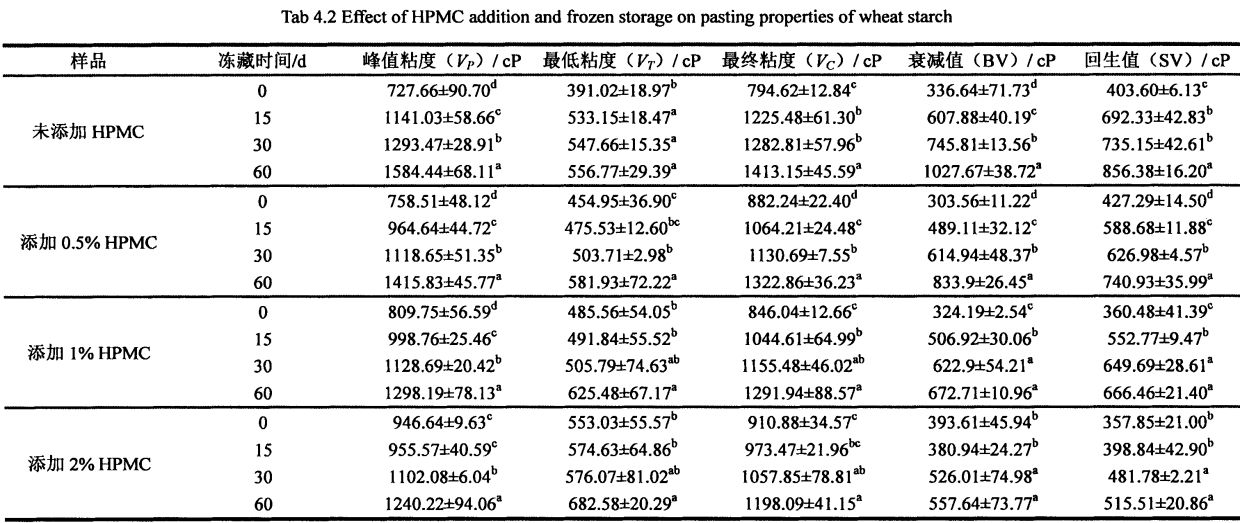
The final viscosity of starch suspension without adding HPMC increased from 794.62 ± 12.84 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1413.15 ± 45.59 CP (frozen storage for 60 days). The peak viscosity of starch suspension increased from 882.24 ± 22.40 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1322.86 ± 36.23 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); the peak viscosity of starch suspension added with 1% HPMC The viscosity increased from 846.04 ± 12.66 CP (frozen storage 0 days) to 1291.94 ± 88.57 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); അധ്യക്ഷത സസ്പെൻഷന്റെ ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ പീക്ക് വിസ്കോസിറ്റി 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി നേടി 91 0.88 ± 34.57 സിപിയിൽ നിന്ന് വർദ്ധിച്ചു
(ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണം 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക്) 1198.09 ± 41.15 CP (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രോസൺ സംഭരണം) വർദ്ധിച്ചു. Correspondingly, the attenuation value of starch suspension without adding HPMC increased from 336.64 ± 71.73 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1027.67 ± 38.72 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); adding 0.5 The attenuation value of starch suspension with %HPMC increased from 303.56±11.22 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 833.9±26.45 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); starch suspension with 1% HPMC added The attenuation value of the liquid was increased from 324.19 ± 2.54 CP (freezing for 0 days) to 672.71 ± 10.96 CP (freezing for 60 days); while adding 2% HPMC,the attenuation value of the starch suspension increased from 393.61 ± 45.94 CP (freezing for 0 days) to 557.64 ± 73.77 CP (freezing for 60 days); while the starch suspension without HPMC added The retrogradation value increased from 403.60 ± 6.13 C
P (frozen storage for 0 days) to 856.38 ± 16.20 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); 0.5% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്ത അധ്യക്ഷത സസ്പെൻഷന്റെ മൂല്യം 427 ൽ നിന്ന് വർദ്ധിച്ചു .29 ± 14.50 സിപി (ഫ്രോസൺ സ്റ്റോറേജ്) 740.93 ± 35.99 സിപി (ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണം); the retrogradation value of starch suspension added with 1% HPMC increased from 360.48±41. 39 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 666.46 ± 21.40 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); അന്നജം സസ്പെൻഷന്റെ പിതൃസമൂഹ മൂല്യം 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തു. 357.85 ± 21.00 സിപി (ഫ്രോസൺ സംഭരണം 60 ദിവസം) 0 ദിവസം) 515.51 ± 20.86 സിപി (60 ദിവസം ഫ്രോസൺ) ആയി ഉയർന്നു.
It can be seen that with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the starch gelatinization characteristics index increased, which is consistent with Tao et a1. f2015) 1. Consistent with the experimental results, they found that with the increase of the number of freeze-thaw cycles, the peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value, and retrogradation value of starch gelatinization all increased to different degrees [166J]. This is mainly because in the process of freezing storage, the amorphous region (Amorphous Region) of starch granules is destroyed by ice crystallization, so that the amylose (the main component) in the amorphous region (non-crystalline region) undergoes phase separation (Phase. separated) phenomenon, and dispersed in the starch suspension, resulting in an increase in the viscosity of starch ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ, അനുബന്ധ അറ്റൻയൂട്ടിന്റെ മൂല്യത്തിലും പിൻവാദ മൂല്യത്തിലും വർദ്ധനവ്. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ അന്നജം ഘടനയെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലൈസേഷന്റെ പ്രഭാവം തടഞ്ഞു. Therefore, the peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value and retrogradation rate of starch gelatinization increased with the addition of HPMC during frozen storage. increase and decrease sequentially.
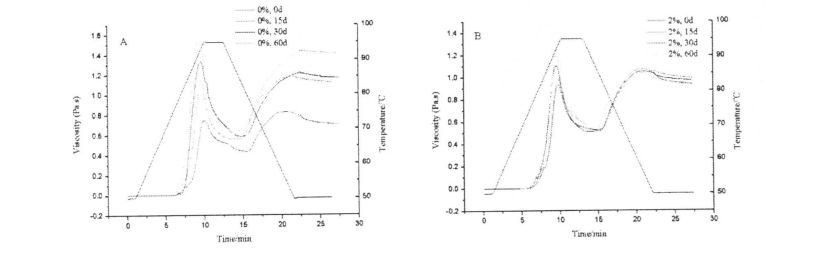
4.3.3 അന്നജം പേസ്റ്റിന്റെ കത്രിക വിഷ്കാലിറ്റിയിലെ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ തുകയും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ സമയവും
ദ്രാവകത്തിന്റെ വിസ്കോസിറ്റി (ഷിയർ വിസ്കോസിറ്റി) കഷൈയർ നിരക്കിന്റെ ഫലം സ്ഥിരമായ ഫ്ലോ ടെസ്റ്റിൽ അന്വേഷിച്ചു, ഒപ്പം ദ്രാവകത്തിന്റെ ഭൗതിക ഘടനയും ഗുണങ്ങളും അതനുസരിച്ച് പ്രതിഫലിച്ചു. Table 4.3 lists the equation parameters obtained by nonlinear fitting, that is, the consistency coefficient K and the flow characteristic index D, as well as the influence of the addition amount of HPMC and the freezing storage time on the above parameters K gate.
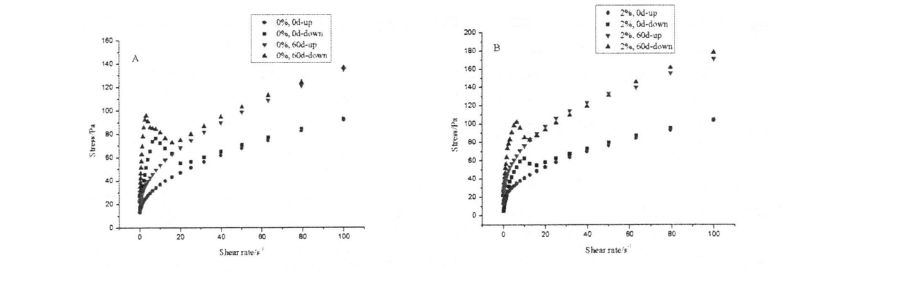
F.2 4.2 എച്ച്പിഎംസി (എ) ഇല്ലാതെ അന്നജം പേസ്റ്റിന്റെ തിംക്സോട്രോപിസം അല്ലെങ്കിൽ 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി (ബി)
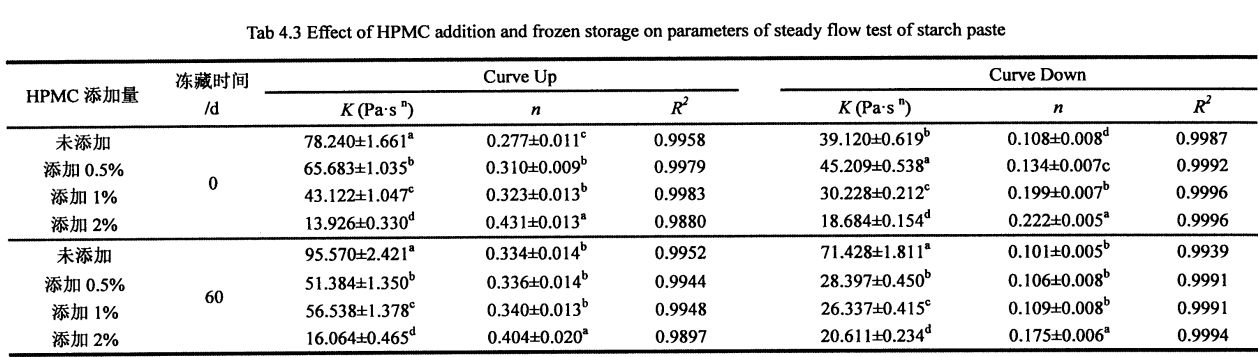
It can be seen from Table 4.3 that all the flow characteristic indices, 2, are less than 1. Therefore, starch paste (whether HPMC is added or whether it is frozen or not) belongs to Pseudoplastic Fluid, and all show shearing Thinning phenomenon (as the shear rate increases, the shear viscosity of the fluid decreases). In addition, the shear rate scans ranged from 0.1 s, respectively. 1 increased to 100 s ~, and then decreased from 100 sd to O. The rheological curves obtained at 1 sd do not completely overlap, and the fitting results of K, s are also different, so the starch paste is a thixotropic pseudoplastic fluid (whether HPMC is added or whether it is frozen or not). However, under the same freezing storage time, with the increase of HPMC addition, the difference between the fitting results of the K n values of the two scans gradually decreased, which indicates that the addition of HPMC makes the structure of starch paste under shear stress. അത് പ്രവർത്തനത്തിൻ കീഴിൽ താരതമ്യേന സ്ഥിരത പുലർത്തുകയും "തിക്സോട്രോപിക് റിംഗ്" കുറയ്ക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു
(തിക്സോട്രോപിക് ലൂപ്പ്) പ്രദേശം, ഇത് ടെംപ്സിരിപോങ്ങിന് സമാനമാണ്, ET a1. (2005) ഇതേ നിഗമനം [167]. This may be mainly because HPMC can form intermolecular cross-links with gelatinized starch chains (mainly amylose chains), which "bound" the separation of amylose and amylopectin under the action of shearing force. , so as to maintain the relative stability and uniformity of the structure (Figure 4.2, the curve with shear rate as abscissa and shear stress as ordinate).
എന്നിരുന്നാലും, സംഭരണ സമയത്തെ മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ നീണ്ടുനിൽക്കുന്ന വ്യത്യസ്ത ഡിഗ്രികളുടെ മൂല്യങ്ങൾ വ്യത്യസ്ത ഡിഗ്രികളായി വർദ്ധിച്ചു, ഇതിൽ യഥാക്രമം 78.611 ന്റെ മൂല്യം വർദ്ധിച്ചു. 2.421 പിഎഎ (60 ദിവസം, 60 ദിവസം), 65.683 ± മുതൽ (O. 5% എച്ച്പിഎംസി) വരെ വർദ്ധിച്ചു. 56.538. 0.277 ± 0.011 (without adding HPMC, 0 days) rose to O. 334±0.014 (no addition, 60 days), increased from 0.310±0.009 (0.5% HPMC added, 0 day) to 0.336±0.014 (0.5% HPMC added, 60 days), from 0.323 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 0 days) to 0.340 ± 0.013 (1% എച്ച്പിഎംസി, 60 ദിവസം), 0.431 ± 0.013 ചേർക്കുക (1% എച്ച്പിഎംസി, 60 ദിവസം) 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി, 0 ദിവസം) മുതൽ 0.404 + 0.020 വരെ (6% എച്ച്പിഎംസി, 60 ദിവസം). താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തുമ്പോൾ, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ സങ്കീർണ്ണതയുടെ വർദ്ധനയോടെ, കെ, കത്തിയുടെ മാറ്റ നിരക്ക് തുടർച്ചയായി കുറയുന്നത് തുടരുന്നു, ഇത് ഷിയറിംഗ് ഫോഴ്സിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തനത്തെ അധ്യക്ഷൻ പേസ്റ്റ് സ്ഥിരീകരിക്കാൻ കഴിയും, ഇത് അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ സവിശേഷതകളുടെ അളവിൽ അന്നജം പേസ്റ്റാക്കിന് കഴിയും. സ്ഥിരത.
ഡൈനാമിക് ഫ്രീക്വൻസി സ്വീപ്പ് മെറ്റീരിയലിന്റെ വിസ്കോലറ്റിറ്റിയെ ഫലപ്രദമായി പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കും, അന്നജം പേസ്റ്റിനായി, അതിന്റെ ജെൽ ശക്തി (ജെൽ ശക്തി) സ്വഭാവമുള്ളതാക്കാൻ ഇത് ഉപയോഗിക്കാം. Figure 4.3 shows the changes of storage modulus/elastic modulus (G') and loss modulus/viscosity modulus (G") of starch gel under the conditions of different HPMC addition and freezing time.
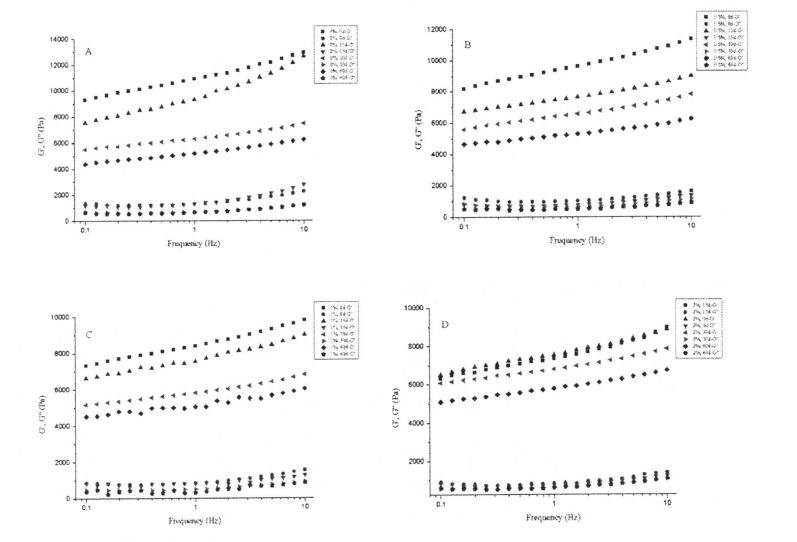
അന്തിമ പേസ്റ്റിന്റെ ഇലാസ്റ്റിക്, വിസ്കോസ് മൊഡ്യൂളുകളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണവും
കുറിപ്പ്: സംഭരണ സമയം മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ വിപുലീകൃത എച്ച്പിഎംസി അന്നജത്തിന്റെ വിസ്കോലറ്റിറ്റിയുടെ മാറ്റാണിത്; B ചേർക്കുന്നതാണ് o. സംഭരണ സമയം മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന 5% എച്ച്പിഎംസി അന്നജത്തിന്റെ മാറ്റം; സിഎച്ച്ഒ സംഭരണ സമയം മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിനൊപ്പം 1% എച്ച്പിഎംസി അന്നജത്തിന്റെ മാറ്റാണിത്. D is the change of the viscoelasticity of 2% HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time
അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈനേഷൻ പ്രക്രിയയ്ക്കൊപ്പം അന്നജം ഗ്രാനുലുകളുടെ ശിഥിലീകരണവും, ക്രിസ്റ്റലൈൻ മേഖലയുടെ തിരോധ്യവും അപ്രത്യക്ഷമാകുന്ന ബോണ്ടിംഗും, അന്നജം. ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിനായുള്ള ചിത്രം 4.3 ൽ കാണിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നതുപോലെ, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവ്, അന്നജം ആരംഭിക്കുമ്പോൾ, ജിഎഎംസി അന്നജ്യകാലത്ത്, ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈസേഷൻ പ്രക്രിയയിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി. അതേസമയം, ചിസാവങ് & സുതാന്തരിക (2005), അന്നജം പേസ്റ്റിന്റെ ജിറത്തും, അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈസ് ചെയ്ത ജി 'എന്നിവയും വ്യത്യസ്ത ഡിഗ്രികളുടെ വിപുലീകൃതമാക്കിയത്. ഇതിന് പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടതാണ്. അന്നജെഡ് ലിങ്കിംഗിന് ശേഷമുള്ള ഇന്റർമോളിക് ക്രോസ് ലിങ്കിംഗിന്റെ അളവ് കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിനും ക്രോസ്-ലിങ്കിംഗിന് ശേഷം ക്രോസ് ലിങ്കിംഗ് ബിരുദം കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിനും അന്നജം (കേടായ അന്നജം) രൂപീകരിക്കുന്നതിന് അന്നജം (കേടായ അന്നജം) കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു. സ്ഥിരതയും കോംപാദനവും സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നത്, ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലുകൾ, പ്രധാനമായും അമിലോപെക്റ്റിൻ, പ്രധാനമായും അമിലോപെക്ടിൻ ചേർന്നതാണ്), അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈസേഷനുശേഷം, തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിന്റെ സംയോജനം, തന്മാത്രാ ശൃംഖലയുടെ കുറവ് mobility), and finally caused the gel strength of starch to decline. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനയോടെ, ജിഎസിന്റെ പ്രവണത അടിച്ചമർത്തപ്പെട്ടു, ഈ പ്രഭാവം എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തുപിടിച്ചു. ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സംഭരണ അവസ്ഥകളിൽ അന്നജത്തിന്റെ ഘടനയിലും സവിശേഷതകളിലും ഐസ് പരലുകളുടെയും ഫലത്തെ തടസ്സപ്പെടുത്തുമെന്ന് എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കൽ ഇത് തടസ്സപ്പെടുത്താൻ കഴിയും.
4.3.5 അന്നജം വീക്കത്തിന്റെ കഴിവിൽ ഐ-ഐപിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർത്ത തുകയും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ സമയവും
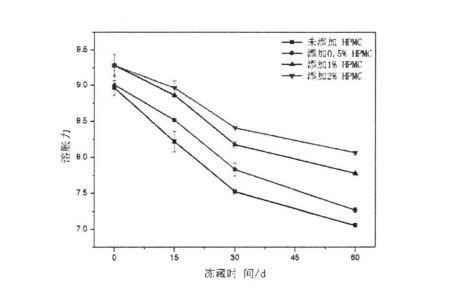
അന്യായത്തിന്റെ വീക്കത്തിന്റെ വീക്കത്തിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെയും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന്റെയും ചിത്രം
അന്നഖത്തിന്റെ ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ ഒരു എൻഡോതെർമിക് കെമിക്കൽ തെർമോഡൈനാമിക് പ്രക്രിയയാണ്. അതിനാൽ, ആന്തരിക താപനില (മരിച്ച താപനില) നിർണ്ണയിക്കാൻ ഡിഎസ്സി പലപ്പോഴും ഉപയോഗിക്കാറുണ്ട്. (ടിസി). Table 4.4 shows the DSC curves of starch gelatinization with 2% and without HPMC added for different freezing storage times.
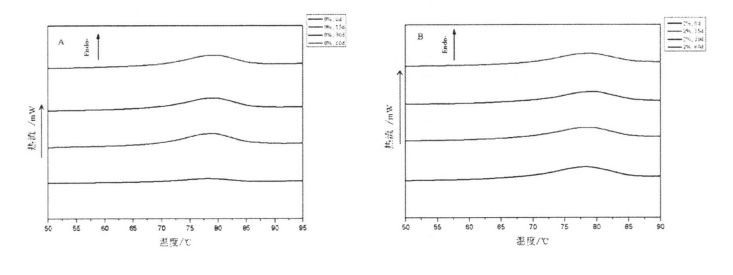
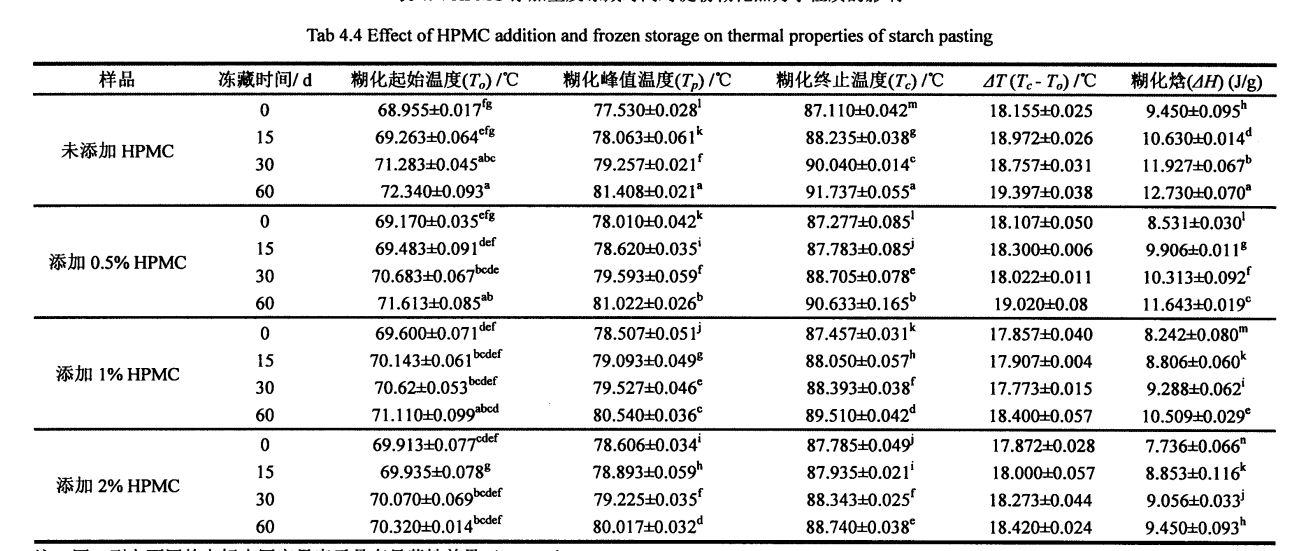
As shown in Table 4.4, for fresh amyloid, with the increase of HPMC addition, starch L has no significant difference, but increases significantly, from 77.530 ± 0.028 (without adding HPMC) to 78.010 ± 0.042 (add 0.5% HPMC), 78.507 ± 0.051 (add 1% HPMC), and 78.606 ± 0.034 (add 2% HPMC), but 4H is significant Decrease, from 9.450 ± 0.095 (without adding HPMC) to 8.53 ± 0.030 (adding 0.5% HPMC), 8.242A: 0.080 (adding 1% HPMC) and 7 .736 ± 0.066 (add 2% HPMC). ഇത് സ ou, et a1 ന് സമാനമാണ്. (2008) found that adding a hydrophilic colloid decreased the starch gelatinization enthalpy and increased the starch gelatinization peak temperature [172]. ഇതിന് പ്രധാനമായും കാരണം എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് മികച്ച ഹൈഡ്രോഫിലിറ്റിറ്റി ഉണ്ട്, അന്നജത്തേക്കാൾ വെള്ളവുമായി സംയോജിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് എളുപ്പമാണ്. അതേസമയം, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ താപ ത്വരിതപ്പെടുത്തിയ ഗ്ലേഷൻ പ്രക്രിയയുടെ വലിയ താപനില കാരണം, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ താപത്തിന്റെ ഉയർന്ന താപനില കാരണം, അന്നജത്തിന്റെ പീക്ക് ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈനൈനൈസേഷൻ താപനില വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുന്നു, ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ എന്തെങ്കിലുമുണ്ടെങ്കിൽ, ജെലാറ്റിനൈസേഷൻ എന്തൽപി കുറയുന്നു.
4.3.7 അന്നഖിന്റെ ആപേക്ഷിക ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റിയിൽ ഐ-ഐപിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെയും സംഭരണ സമയത്തിന്റെ ഫലങ്ങൾ
ചിത്രം 4.6. As shown in A, the positions of the starch crystallization peaks are located at 170, 180, 190 and 230, respectively, and there is no significant change in the peak positions regardless of whether they are treated by freezing or adding HPMC. This shows that, as an intrinsic property of wheat starch crystallization, the crystalline form remains stable.
എന്നിരുന്നാലും, സംഭരണ സമയത്തെ മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ നീണ്ട, അന്തന്തിന്റെ ആന്തരിക ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റി 20.40 + 0.14 ൽ നിന്ന് (എച്ച്പിഎംസി, 0 ദിവസം) മുതൽ 36.50 വരെ വർദ്ധിച്ചു (എച്ച്പിഎംസി, ശീതീകരിച്ച്, ശീതീകരിച്ച്, ശീതീകരിച്ച്, ഫ്രോസൺ സ്റ്റോറേജ് ഇല്ലാതെ). 60 days), and increased from 25.75 + 0.21 (2% HPMC added, 0 days) to 32.70 ± 0.14 (2% HPMC added, 60 days) (Figure 4.6.B), this and Tao, et a1. (2016), the change rules of the measurement results are consistent [173-174]. ആപേക്ഷിക ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റിയുടെ വർദ്ധനവ് പ്രധാനമായും മര്ഫസ് മേഖലയുടെ നാശവും ക്രിസ്റ്റലിൻ മേഖലയുടെ ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റിയുടെ വർദ്ധനവുമാണ്. കൂടാതെ, അന്നജം ജെലാറ്റിനൈനൈസേഷന്റെ തെർമഡൈനാമിക് ഗുണങ്ങളിലെ മാറ്റങ്ങളുടെ നിഗമനവുമായി പൊരുത്തപ്പെടുന്ന ആപേക്ഷിക ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റിയുടെ അളവ് വർദ്ധിച്ചു, ഇത് ഫ്രീച്ചിംഗ് പ്രക്രിയയുടെ അരംഭത്തിന്റെ ഘടനാപരമായ നാശവും, അതിന്റെ ഘടനയും സ്വന്തമാക്കി.
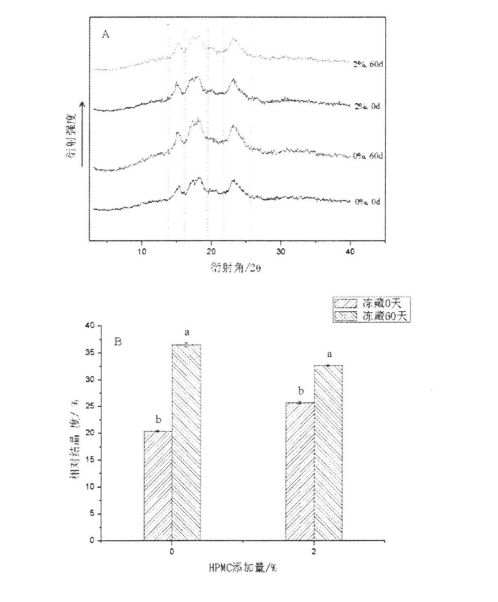
XRD പ്രോപ്പർട്ടികളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലും ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണവും ചിത്രം 4.6
കുറിപ്പ്: a x ആണ്. X-ray diffraction pattern; ബിദ്രച്ചിന്റെ ആപേക്ഷിക ക്രിസ്റ്റലിറ്റി ഫലമാണ് ബി;
4.4 അധ്യായം സംഗ്രഹം
5.1 ആമുഖം
Yeast is a unicellular eukaryotic microorganism, its cell structure includes cell wall, cell membrane, mitochondria, etc., and its nutritional type is a facultative anaerobic microorganism. അനാരോബിക് അവസ്ഥകളിൽ, അത് മദ്യവും energy ർജ്ജവും ഉത്പാദിപ്പിക്കുന്നു, അതേസമയം കാർബൺ ഡൈ ഓക്സൈഡ്, വെള്ളം, energy ർജ്ജം എന്നിവ സൃഷ്ടിക്കാൻ കഴിഞ്ഞുമാറുന്നു.
In the case of frozen storage, yeast will be affected by environmental stress and affect its viability. When the freezing rate is too high, the water in the system will rapidly crystallize and increase the external osmotic pressure of the yeast, thereby causing the cells to lose water; when the freezing rate is too high. ഇത് വളരെ കുറവാണെങ്കിൽ, ഐസ് പരലുകൾ വളരെ വലുതും യീസ്റ്റ് ഞെക്കിയിടുകയും സെൽ മതിൽ നശിപ്പിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യും; രണ്ടും യീസ്റ്റിന്റെ അതിജീവന നിരക്കും അതിന്റെ അഴുകൽ പ്രവർത്തനവും കുറയ്ക്കും. In addition, many studies have found that after the yeast cells are ruptured due to freezing, they will release a reducing substance-reduced glutathione, which in turn reduces the disulfide bond to a sulfhydryl group, which will eventually destroy the network structure of gluten protein, resulting in a decrease in the quality of pasta products [176-177].
കാരണം എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് ശക്തമായ ജല നിലനിർത്തലും വെള്ളവും കൈവശമുള്ള ശേഷിയുണ്ടെന്നും, ഡാവ് സിസ്റ്റത്തിൽ ചേർക്കുന്നത് ഐസ് ക്രിസ്റ്റലുകളുടെ രൂപവത്കരണത്തെയും വളർച്ചയെയും തടയാൻ കഴിയും. ഈ പരീക്ഷണത്തിൽ, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ വ്യത്യസ്ത അളവിൽ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ചേർത്തു, ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണത്തിന് ശേഷം, ക്രൂരമായ സാഹചര്യങ്ങളിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ സംരക്ഷണ പ്രഭാവം വിലയിരുത്താൻ നിർണ്ണയിച്ചു.
5.2 മെറ്റീരിയലുകളും രീതികളും
5.2.1 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക വസ്തുക്കളും ഉപകരണങ്ങളും
മെറ്റീരിയലുകളും ഉപകരണങ്ങളും
BPS. 500 ക്ലൂ നിരന്തരമായ താപനിലയും ഈർപ്പം ബോക്സും
3 മി സോളിഡ് ഫിലിം കോളനി റാപ്പിഡ് കൗണ്ട് ടെസ്റ്റ് പീസ്
SP. മോഡൽ 754 യുവി സ്പെക്ട്രോഫോട്ടോമീറ്റർ
അൾട്രാ-വൃത്തിയുള്ള അണുവിമുക്തമായ ഓപ്പറേറ്റിംഗ് പട്ടിക
കെഡിസി. 160 മണിക്കൂർ അതിവേഗ ശീതീകരിച്ച സെൻട്രിഫ്യൂജ്
Zwy-240 നിരന്തരമായ താപനില ഇൻകുബേറ്റർ
ബിഡിഎസ്. 200 Inverted Biological Microscope
നിര്മ്മാതാവ്
ഏഞ്ചൽ യീസ്റ്റ് കോ., ലിമിറ്റഡ്
3 മി കോർപ്പറേഷൻ ഓഫ് അമേരിക്ക
ഷാങ്ഹായ് സ്പെക്ട്രം ശാസ്ത്രീയ ഉപകരണ കോ., ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ജിയാങ്സു ടോങ്ജിംഗ് ശുദ്ധീകരണ ഉപകരണങ്ങൾ കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ചോങ്കിംഗ് ഓട്ടോ ഒപ്റ്റിക്കൽ ഇൻസ്ട്രുമെന്റ് കമ്പനി, ലിമിറ്റഡ്
5.2.2 പരീക്ഷണാത്മക രീതി
5.2.2.1 യീസ്റ്റ് ദ്രാവകം തയ്യാറാക്കൽ
മെസിയാനി, എറ്റ് എ 1 കാണുക. (2012) ന്റെ പരീക്ഷണ രീതി [ഉദ്ധരിച്ചത്, നേരിയ പരിഷ്കാരങ്ങൾ. 50 മില്ലി ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 50 ഗ്രാം ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ട്യൂബിന്റെ അടിയിൽ 1.5 സെന്റിമീറ്റർ ഉയരത്തിൽ അമർത്തുക, തുടർന്ന് അത് ഒരു മില്ലിമീറ്റർ ഭരണാധികാരിയുടെയും 85% നും ഇൻകുനേറ്റ് ചെയ്യുക, ഒരു മില്ലിമീറ്റർ ഭരണാധികാരിയുടെ തെളിവ് നൽകുക (ദശാംശസ്ഥാനത്തിന് ശേഷം കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 85%. പ്രൂഫിംഗിന് ശേഷം അസമമായ മുകളിലെ അറ്റത്തുള്ള സാമ്പിളുകൾക്കായി, അവരുടെ അനുബന്ധ ഉയരങ്ങൾ അളക്കുന്നതിന് തുല്യ ഇടവേളകളിൽ 3 അല്ലെങ്കിൽ 4 പോയിന്റുകൾ തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുക (ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്, ഓരോ 900), അളന്ന ഉയരം മൂല്യങ്ങൾ ശരാശരി. ഓരോ സാമ്പിളിലും മൂന്ന് തവണ സമാന്തരമായി.
5.2.2.3 സി.എഫ്.യു (കോളനി-രൂപീകരിക്കുന്ന യൂണിറ്റുകൾ) എണ്ണം
Weigh 1 g of dough, add it to a test tube with 9 mL of sterile normal saline according to the requirements of the aseptic operation, shake it fully, record the concentration gradient as 101, and then dilute it into a series of concentration gradients until 10'1. Draw 1 mL of dilution from each of the above tubes, add it to the center of the 3M yeast rapid count test piece (with strain selectivity), and place the above test piece in a 25°C incubator according to the operating requirements and culture conditions specified by 3M. 5 d, take out after the end of the culture, first observe the colony morphology to determine whether it conforms to the colony characteristics of yeast, and then count and microscopically examine [179]. ഓരോ സാമ്പിളും മൂന്ന് തവണ ആവർത്തിച്ചു.
The alloxan method was used to determine the glutathione content. The principle is that the reaction product of glutathione and alloxan has an absorption peak at 305 nl. Specific determination method: pipette 5 mL of yeast solution into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, then centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 min, take 1 mL of supernatant into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, add 1 mL of 0.1 mol/mL to the tube L alloxan solution, mixed thoroughly, then add 0.2 M PBS (pH 7.5) and 1 mL of 0.1 M, NaOH solution to it, mix well, let stand for 6 min, and immediately add 1 M, NaOH The solution was 1 mL, and the absorbance at 305 nm was measured with a UV spectrophotometer after thorough mixing. ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ ഉള്ളടക്കം സ്റ്റാൻഡേർഡ് വക്രത്തിൽ നിന്ന് കണക്കാക്കി. Each sample was paralleled three times.
5.3.1 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർത്ത തുകയുടെ സ്വാധീനം, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ പ്രൂഹ ഉയരത്തിൽ ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണ സമയവും

ചിത്രം 5.1 ൽ കാണിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നതുപോലെ, 0 ദിവസം ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത പോലെ, എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ അളവിൽ, കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 1,234-0.11 സെന്റിമീറ്റർ വരെ 4.274 സെന്റിമീറ്റർ വരെ 4.274 സെന്റിമീത്തേക്ക് ഉയർന്നു. -0.12 സെ.മീ. ചേർത്തു (1% എച്ച്പിഎംസിഐ), 4.314-0.19 സെ.മീ. (2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തു), ഇത് പ്രധാനമായും എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിനെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കിയുള്ളതായിരിക്കാം (അധ്യായം 2) സവിശേഷതകൾ (അധ്യായം 2 കാണുക). However, after being frozen for 60 days, the proofing height of the dough decreased to varying degrees. പ്രത്യേകിച്ചും, എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഇല്ലാതെ കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഇല്ലാതെ 4.234-0.11 സെന്റിമീറ്റർ (ഫ്രീസിംഗ് 0 ദിവസം) 3 .18 + 0.15 സെ.മീ വരെ (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സംഭരണം); 0.5% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഉപയോഗിച്ച് കുഴെച്ചതു ചേർത്ത് 4.27 + 0.12 സെ.മീ. മുതൽ 3.424-0.22 സെ. 60 days); കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ 1% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്ത് ചേർത്തു 1% എച്ച്പിഎംസി 4.314-0.19 സെ.മീ. മുതൽ 3.774-0.12 സെ.മീ വരെ (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണം); 2% എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഉപയോഗിച്ച് കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ചേർത്തപ്പോൾ. ഹെയർ ഉയരം 4.594-0.17 സെന്റിമീറ്റർ (ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത സ്റ്റോറേജ്) വരെ കുറഞ്ഞു (ഫ്രോസൺ സ്റ്റോറേജ്) മുതൽ 4.09- വരെ) വരെ കുറഞ്ഞു (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണം). കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ കുറയുന്നതിന്റെ അളവ് കുറയുന്നു, ക്രമേണ കുറയുന്നു. This shows that under the condition of frozen storage, HPMC can not only maintain the relative stability of the dough network structure, but also better protect the survival rate of yeast and its fermentation gas production activity, thereby reducing the quality deterioration of fermented noodles.
5.3.2 യീസ്റ്റ് അതിജീവന നിരക്കിലെ ഐ-ഐപിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെയും ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുന്ന സമയത്തിന്റെയും ഫലം
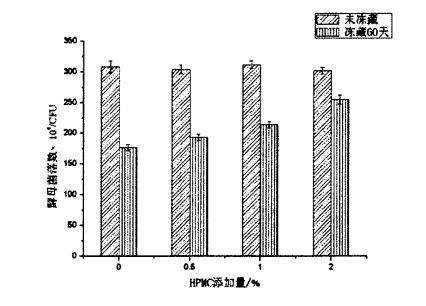
ചിത്രം 5.2 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെയും അതിജീവനത്തിന്റെ ഭൂണ്ണായിയിലെ ഫ്രോസൺ സ്റ്റോറേജും
ചിത്രം 5.3 യീസ്റ്റുകളുടെ മൈക്രോഗ്രാഫ്
5.3.3 കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെയും മരവിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സമയത്തിന്റെയും ഫലങ്ങൾ
Glutathione is a tripeptide compound composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, and has two types: reduced and oxidized. യീസ്റ്റ് സെൽ ഘടന നശിപ്പിക്കുകയും മരിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുമ്പോൾ, സെല്ലുകളുടെ പ്രവേശനക്ഷമത വർദ്ധിക്കുന്നു, ഇൻട്രാ സെല്ലുലാർ ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ സെല്ലിന് പുറത്ത് പുറത്തിറക്കി, അത് കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു. കുറഞ്ഞ ഗ്ലാറ്റാത്താണോ, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീനുകളുടെ ക്രോസ്-ലിങ്കിംഗ് രൂപീകരിക്കുന്നത്, ഗ്ലൂറ്റൻ പ്രോട്ടീനുകളുടെ ക്രോസ്-ലിങ്ക് ചെയ്യുന്നയാൾ (-ss-) രൂപപ്പെടുത്തുന്നത്, സൾഫ്ഹൈഡ്രിൾ ഗ്രൂപ്പുകൾ (.ഷുചെയ്യുക നെറ്റ്വർക്ക് ഘടനയെ) രൂപീകരിക്കാൻ ബ്രേക്ക് ചെയ്തു. stability and integrity, and ultimately lead to the deterioration of the quality of fermented flour products. Usually, under environmental stress (such as low temperature, high temperature, high osmotic pressure, etc.), yeast will reduce its own metabolic activity and increase its stress resistance, or produce spores at the same time. When the environmental conditions are suitable for its growth and reproduction again, then restore the metabolism and proliferation vitality. However, some yeasts with poor stress resistance or strong metabolic activity will still die if they are kept in a frozen storage environment for a long time.
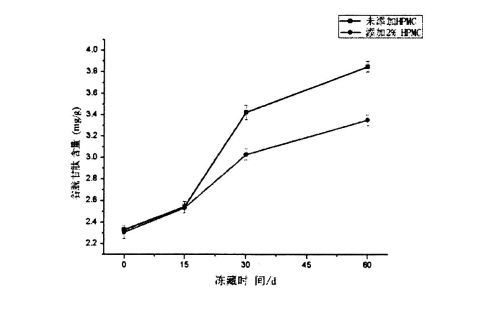
FIG 5.4 എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ പ്രഭാവം ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ (ജിഎസ്എച്ച്) ഉള്ളടക്കത്തിൽ ഫ്രോസൺ സ്റ്റോറേജ്
As shown in Figure 5.4, the glutathione content increased regardless of whether HPMC was added or not, and there was no significant difference between the different addition amounts. കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ മോശം സമ്മർദ്ദ പ്രതിരോധവും സഹിഷ്ണുതയും ഉണ്ടാക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ആക്റ്റീവ് ഡ്രൈ യീസ്റ്റ് ബാധിച്ചതിനാലാകാം ഇത്. Under the condition of low temperature freezing, the cells die, and then glutathione is released, which is only related to the characteristics of the yeast itself. ഇത് ബാഹ്യ പരിതസ്ഥിതിയുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്നു, പക്ഷേ എച്ച്പിഎംസി ചേർത്തവയുമായി യാതൊരു ബന്ധവുമില്ല. അതിനാൽ, ഫ്രീസുചെയ്യുന്നതിന്റെ 15 ദിവസത്തിനുള്ളിൽ ഗ്ലൂട്ടതിയോണിന്റെ ഉള്ളടക്കം വർദ്ധിച്ചു, രണ്ടും തമ്മിൽ കാര്യമായ വ്യത്യാസമില്ല. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, ഫ്രീസുണാകൃതിയിലുള്ള സമയത്തിന്റെ കൂടുതൽ വിപുലീകരണത്തോടെ, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവ്, എച്ച്പിഎംസി കൂട്ടിച്ചേർക്കലിന്റെ വർദ്ധനവ് 2.329 എ മുതൽ എച്ച്പിഎംസി ഇല്ലാത്ത ഉള്ളടക്കം 2.329 എ വരെ വർദ്ധിച്ചു (0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് 0 ദിവസത്തേക്ക്) വർദ്ധിച്ചു (0.040.0.051) ആയി (6 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ഫ്രോസൺ സംഭരണം) (60 ദിവസത്തേക്ക് ശീതീകരിച്ച സംഭരണം); while the yeast liquid added 2% HPMC, its glutathione content increased from 2.307+0 .058 mg/g (frozen storage for 0 days) rose to 3.351+0.051 mg/g (frozen storage for 60 days). യീസ്റ്റ് കോശങ്ങളെ സംരക്ഷിക്കുന്നതിനും യീസ്റ്റിന്റെ മരണം കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിനും എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് കഴിയുമെന്ന് ഇത് കൂടുതൽ സൂചിപ്പിച്ചു, അതുവഴി സെല്ലിന് പുറത്തുവിട്ട ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോണിന്റെ ഉള്ളടക്കം കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു. ഐസ് പരലുകളുടെ എണ്ണം എച്ച്പിഎംസിക്ക് കുറയാനാകുന്നതിനാണിത്, അതുവഴി ഐസ് പരലുകളുടെ സമ്മർദ്ദം യീസ്റ്റിലേക്ക് ഫലപ്രദമായി കുറയ്ക്കുകയും ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തിയോൺ പുറത്തിറങ്ങുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
5.4 അധ്യായം സംഗ്രഹം
Yeast is an indispensable and important component in fermented flour products, and its fermentation activity will directly affect the quality of the final product. ഈ പരീക്ഷയിൽ, ഫ്രീസുചെയ്ത കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ സിസ്റ്റത്തിലെ എച്ച്പിഎംസിയുടെ സംരക്ഷണ ഫലങ്ങൾ വിലയിരുത്തി, യീസ്റ്റ് ഫെർമെന്റേഷൻ പ്രവർത്തനം, ശീതീകരിച്ച കുഴെച്ചതുമുതൽ എക്സ്ട്രാസെല്ലുലാർ ഗ്ലൂട്ടത്തയോൺ ഉള്ളടക്കം എന്നിവ പഠിച്ചുകൊണ്ട് വിലയിരുത്തി. Through experiments, it was found that the addition of HPMC can better maintain the fermentation activity of the yeast, and reduce the degree of decline in the proofing height of the dough after 60 days of freezing, thus providing a guarantee for the specific volume of the final product; in addition, the addition of HPMC effectively The decrease of yeast survival number was inhibited and the increase rate of reduced glutathione content was reduced, thereby alleviating the damage of glutathione to dough network structure. This suggests that HPMC can protect yeast by inhibiting the formation and growth of ice crystals.
പോസ്റ്റ് സമയം: ഒക്ടോബർ -08-2022